#python pandas how to delete a column
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
How to Drop a Column in Python: Simplifying Data Manipulation
Dive into our latest post on 'Drop Column Python' and master the art of efficiently removing DataFrame columns in Python! Perfect for data analysts and Python enthusiasts. #PythonDataFrame #DataCleaning #PandasTutorial 🐍🔍
Hello, Python enthusiasts and data analysts! Today, we’re tackling a vital topic in data manipulation using Python – how to effectively use the Drop Column Python method. Whether you’re a seasoned programmer or just starting out, understanding this technique is crucial in data preprocessing and analysis. In this post, we’ll delve into the practical use of the drop() function, specifically…
View On WordPress
#DataFrame Column Removal#how to delete a column from dataframe in python#how to drop column in python#how to remove a column from a dataframe in python#Pandas Drop Column#pandas how to remove a column#Python Data Cleaning#python pandas how to delete a column
0 notes
Text
4th week: plotting variables
I put here as usual the python script, the results and the comments:
Python script:
Created on Tue Jun 3 09:06:33 2025
@author: PabloATech """
libraries/packages
import pandas import numpy import seaborn import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
read the csv table with pandas:
data = pandas.read_csv('C:/Users/zop2si/Documents/Statistic_tests/nesarc_pds.csv', low_memory=False)
show the dimensions of the data frame:
print() print ("length of the dataframe (number of rows): ", len(data)) #number of observations (rows) print ("Number of columns of the dataframe: ", len(data.columns)) # number of variables (columns)
variables:
variable related to the background of the interviewed people (SES: socioeconomic status):
biological/adopted parents got divorced or stop living together before respondant was 18
data['S1Q2D'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S1Q2D'], errors='coerce')
variable related to alcohol consumption
HOW OFTEN DRANK ENOUGH TO FEEL INTOXICATED IN LAST 12 MONTHS
data['S2AQ10'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S2AQ10'], errors='coerce')
variable related to the major depression (low mood I)
EVER HAD 2-WEEK PERIOD WHEN FELT SAD, BLUE, DEPRESSED, OR DOWN MOST OF TIME
data['S4AQ1'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S4AQ1'], errors='coerce')
NUMBER OF EPISODES OF PATHOLOGICAL GAMBLING
data['S12Q3E'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S12Q3E'], errors='coerce')
HIGHEST GRADE OR YEAR OF SCHOOL COMPLETED
data['S1Q6A'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S1Q6A'], errors='coerce')
Choice of thee variables to display its frequency tables:
string_01 = """ Biological/adopted parents got divorced or stop living together before respondant was 18: 1: yes 2: no 9: unknown -> deleted from the analysis blank: unknown """
string_02 = """ HOW OFTEN DRANK ENOUGH TO FEEL INTOXICATED IN LAST 12 MONTHS
Every day
Nearly every day
3 to 4 times a week
2 times a week
Once a week
2 to 3 times a month
Once a month
7 to 11 times in the last year
3 to 6 times in the last year
1 or 2 times in the last year
Never in the last year
Unknown -> deleted from the analysis BL. NA, former drinker or lifetime abstainer """
string_02b = """ HOW MANY DAYS DRANK ENOUGH TO FEEL INTOXICATED IN THE LAST 12 MONTHS: """
string_03 = """ EVER HAD 2-WEEK PERIOD WHEN FELT SAD, BLUE, DEPRESSED, OR DOWN MOST OF TIME:
Yes
No
Unknown -> deleted from the analysis """
string_04 = """ NUMBER OF EPISODES OF PATHOLOGICAL GAMBLING """
string_05 = """ HIGHEST GRADE OR YEAR OF SCHOOL COMPLETED
No formal schooling
Completed grade K, 1 or 2
Completed grade 3 or 4
Completed grade 5 or 6
Completed grade 7
Completed grade 8
Some high school (grades 9-11)
Completed high school
Graduate equivalency degree (GED)
Some college (no degree)
Completed associate or other technical 2-year degree
Completed college (bachelor's degree)
Some graduate or professional studies (completed bachelor's degree but not graduate degree)
Completed graduate or professional degree (master's degree or higher) """
replace unknown values for NaN and remove blanks
data['S1Q2D']=data['S1Q2D'].replace(9, numpy.nan) data['S2AQ10']=data['S2AQ10'].replace(99, numpy.nan) data['S4AQ1']=data['S4AQ1'].replace(9, numpy.nan) data['S12Q3E']=data['S12Q3E'].replace(99, numpy.nan) data['S1Q6A']=data['S1Q6A'].replace(99, numpy.nan)
create a recode for number of intoxications in the last 12 months:
recode1 = {1:365, 2:313, 3:208, 4:104, 5:52, 6:36, 7:12, 8:11, 9:6, 10:2, 11:0} data['S2AQ10'] = data['S2AQ10'].map(recode1)
print(" ") print("Statistical values for varible 02 alcohol intoxications of past 12 months") print(" ") print ('mode: ', data['S2AQ10'].mode()) print ('mean', data['S2AQ10'].mean()) print ('std', data['S2AQ10'].std()) print ('min', data['S2AQ10'].min()) print ('max', data['S2AQ10'].max()) print ('median', data['S2AQ10'].median()) print(" ") print("Statistical values for highest grade of school completed") print ('mode', data['S1Q6A'].mode()) print ('mean', data['S1Q6A'].mean()) print ('std', data['S1Q6A'].std()) print ('min', data['S1Q6A'].min()) print ('max', data['S1Q6A'].max()) print ('median', data['S1Q6A'].median()) print(" ")
plot01 = seaborn.countplot(x="S2AQ10", data=data) plt.xlabel('Alcohol intoxications past 12 months') plt.title('Alcohol intoxications in the Past 12 Months in the NESARC Study')
plot02 = seaborn.countplot(x="S1Q6A", data=data) plt.xlabel('Highest grade (1-14)') plt.title('Highest grade or year of school completed')
I create a copy of the data to be manipulated later
sub1 = data[['S2AQ10','S1Q6A']]
create bins for no intoxication, few intoxications, …
data['S2AQ10'] = pandas.cut(data.S2AQ10, [0, 6, 36, 52, 104, 208, 365], labels=["very few","some", "often", "quite often", "very often", "permanent"])
change format from numeric to categorical
data['S2AQ10'] = data['S2AQ10'].astype('category')
print ('intoxication category counts') c1 = data['S2AQ10'].value_counts(sort=False, dropna=True) print(c1)
bivariate bar graph C->Q
plot03 = seaborn.catplot(x="S2AQ10", y="S1Q6A", data=data, kind="bar", ci=None) plt.xlabel('Alcohol intoxications') plt.ylabel('Highest grade')
c4 = data['S1Q6A'].value_counts(sort=False, dropna=False) print("c4: ", c4) print(" ")
I do sth similar but the way around:
creating 3 level education variable
def edu_level_1 (row): if row['S1Q6A'] <9 : return 1 # high school if row['S1Q6A'] >8 and row['S1Q6A'] <13 : return 2 # bachelor if row['S1Q6A'] >12 : return 3 # master or higher
sub1['edu_level_1'] = sub1.apply (lambda row: edu_level_1 (row),axis=1)
change format from numeric to categorical
sub1['edu_level'] = sub1['edu_level'].astype('category')
plot04 = seaborn.catplot(x="edu_level_1", y="S2AQ10", data=sub1, kind="boxen") plt.ylabel('Alcohol intoxications in the past 12 months') plt.xlabel('Highest grade') plt.grid() plt.show()
Results and comments:
length of the dataframe (number of rows): 43093 Number of columns of the dataframe: 3008
Statistical values for variable "alcohol intoxications of past 12 months":
mode: 0 0.0 dtype: float64 mean 9.115493905630748 std 40.54485720135516 min 0.0 max 365.0 median 0.0
Statistical values for variable "highest grade of school completed":
mode 0 8 dtype: int64 mean 9.451024528345672 std 2.521281770664422 min 1 max 14 median 10.0
intoxication category counts very few 6026 some 2042 often 510 quite often 272 very often 184 permanent 276 Name: S2AQ10, dtype: int64
c4: (counts highest grade)
8 10935 6 1210 12 5251 14 3257 10 8891 13 1526 7 4518 11 3772 5 414 4 931 3 421 9 1612 2 137 1 218 Name: S1Q6A, dtype: int64
Plots: Univariate highest grade:
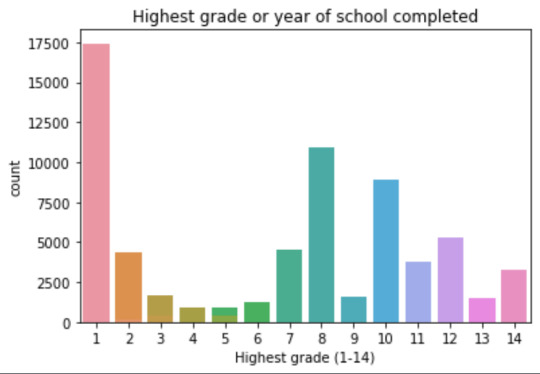
mean 9.45 std 2.5
-> mean and std. dev. are not very useful for this category-distribution. Most interviewed didn´t get any formal schooling, the next larger group completed the high school and the next one was at some college but w/o degree.
Univariate number of alcohol intoxications:
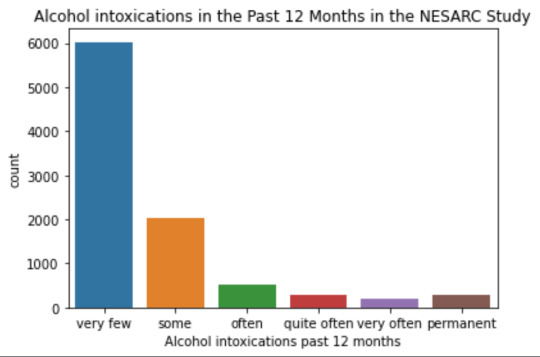
mean 9.12 std 40.54
-> very left skewed, most of the interviewed persons didn´t get intoxicated at all or very few times in the last 12 months (as expected)
Bivariate: the one against the other:
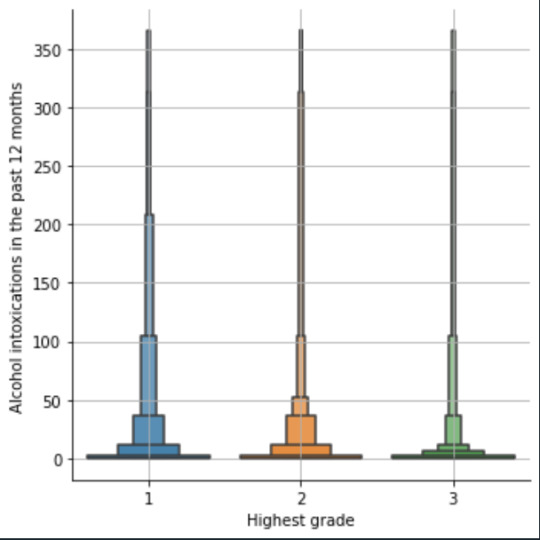
This bivariate plot shows three categories:
1: high school or lower
2: high school to bachelor
3: master or PhD
And the frequency of alcohol intoxications in the past 12 months.
The number of intoxications is higher in the group 1 for all the segments, but from 1 to 3 every group shows occurrences in any number of intoxications. More information and a more detailed analysis would be necessary to make conclusions.
0 notes
Text
Pandas DataFrame Cleanup: Master the Art of Dropping Columns Data cleaning and preprocessing are crucial steps in any data analysis project. When working with pandas DataFrames in Python, you'll often encounter situations where you need to remove unnecessary columns to streamline your dataset. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore various methods to drop columns in pandas, complete with practical examples and best practices. Understanding the Basics of Column Dropping Before diving into the methods, let's understand why we might need to drop columns: Remove irrelevant features that don't contribute to analysis Eliminate duplicate or redundant information Clean up data before model training Reduce memory usage for large datasets Method 1: Using drop() - The Most Common Approach The drop() method is the most straightforward way to remove columns from a DataFrame. Here's how to use it: pythonCopyimport pandas as pd # Create a sample DataFrame df = pd.DataFrame( 'name': ['John', 'Alice', 'Bob'], 'age': [25, 30, 35], 'city': ['New York', 'London', 'Paris'], 'temp_col': [1, 2, 3] ) # Drop a single column df = df.drop('temp_col', axis=1) # Drop multiple columns df = df.drop(['city', 'age'], axis=1) The axis=1 parameter indicates we're dropping columns (not rows). Remember that drop() returns a new DataFrame by default, so we need to reassign it or use inplace=True. Method 2: Using del Statement - The Quick Solution For quick, permanent column removal, you can use Python's del statement: pythonCopy# Delete a column using del del df['temp_col'] Note that this method modifies the DataFrame directly and cannot be undone. Use it with caution! Method 3: Drop Columns Using pop() - Remove and Return The pop() method removes a column and returns it, which can be useful when you want to store the removed column: pythonCopy# Remove and store a column removed_column = df.pop('temp_col') Advanced Column Dropping Techniques Dropping Multiple Columns with Pattern Matching Sometimes you need to drop columns based on patterns in their names: pythonCopy# Drop columns that start with 'temp_' df = df.drop(columns=df.filter(regex='^temp_').columns) # Drop columns that contain certain text df = df.drop(columns=df.filter(like='unused').columns) Conditional Column Dropping You might want to drop columns based on certain conditions: pythonCopy# Drop columns with more than 50% missing values threshold = len(df) * 0.5 df = df.dropna(axis=1, thresh=threshold) # Drop columns of specific data types df = df.select_dtypes(exclude=['object']) Best Practices for Dropping Columns Make a Copy First pythonCopydf_clean = df.copy() df_clean = df_clean.drop('column_name', axis=1) Use Column Lists for Multiple Drops pythonCopycolumns_to_drop = ['col1', 'col2', 'col3'] df = df.drop(columns=columns_to_drop) Error Handling pythonCopytry: df = df.drop('non_existent_column', axis=1) except KeyError: print("Column not found in DataFrame") Performance Considerations When working with large datasets, consider these performance tips: Use inplace=True to avoid creating copies: pythonCopydf.drop('column_name', axis=1, inplace=True) Drop multiple columns at once rather than one by one: pythonCopy# More efficient df.drop(['col1', 'col2', 'col3'], axis=1, inplace=True) # Less efficient df.drop('col1', axis=1, inplace=True) df.drop('col2', axis=1, inplace=True) df.drop('col3', axis=1, inplace=True) Common Pitfalls and Solutions Dropping Non-existent Columns pythonCopy# Use errors='ignore' to skip non-existent columns df = df.drop('missing_column', axis=1, errors='ignore') Chain Operations Safely pythonCopy# Use method chaining carefully df = (df.drop('col1', axis=1) .drop('col2', axis=1) .reset_index(drop=True)) Real-World Applications Let's look at a practical example of cleaning a dataset: pythonCopy# Load a messy dataset df = pd.read_csv('raw_data.csv')
# Clean up the DataFrame df_clean = (df.drop(columns=['unnamed_column', 'duplicate_info']) # Remove unnecessary columns .drop(columns=df.filter(regex='^temp_').columns) # Remove temporary columns .drop(columns=df.columns[df.isna().sum() > len(df)*0.5]) # Remove columns with >50% missing values ) Integration with Data Science Workflows When preparing data for machine learning: pythonCopy# Drop target variable from features X = df.drop('target_variable', axis=1) y = df['target_variable'] # Drop non-numeric columns for certain algorithms X = X.select_dtypes(include=['float64', 'int64']) Conclusion Mastering column dropping in pandas is essential for effective data preprocessing. Whether you're using the simple drop() method or implementing more complex pattern-based dropping, understanding these techniques will make your data cleaning process more efficient and reliable. Remember to always consider your specific use case when choosing a method, and don't forget to make backups of important data before making permanent changes to your DataFrame. Now you're equipped with all the knowledge needed to effectively manage columns in your pandas DataFrames. Happy data cleaning!
0 notes
Text
Google translate bot text to speech

#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH HOW TO#
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH DOWNLOAD#
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH FREE#
The playsound module is then used to play the generated mp3 file, After that, the generated mp3 file is deleted using the os module. It converts text from one language to another language and saves its mp3 recorded file. Choose your preferred engine, language, speech rate, and pitch.
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH DOWNLOAD#
When it is all done, you can click the download button to download your voice over as an mp3 file. Set back and wait for a few seconds while our AI algorithm does its text to speech magic to convert your text into an awesome voice over. It is created using google’s googleTrans API and speech_recognition library of python. Select Accessibility and then Text-to-speech output. Just type some text, select the language, the voice and the speech style and emotion, then hit the Play button. gTTs: The gTTS API supports several languages including English, Hindi, Tamil, French, German and many more.Ī real-time voice translator that can translate voice input and give translated voice output generated from it.
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH FREE#
googletrans: Googletrans is a free and unlimited python library that implemented Google Translate API.
We have to use pip for Speech Recognition. Wait for a second if it didn't play your voice maybe your connection is slow. The voices vary depending on your browser.
Speech Recognition Module: It is a library with the help of which Python can recognize the command given. Type a message below then click 'Speak' and SpeechSynthesis will read it out.
playsound: This module is used to play sound in Python.
Taking multiple inputs from user in Python.
Python | Program to convert String to a List.
isupper(), islower(), lower(), upper() in Python and their applications.
Print lists in Python (5 Different Ways).
Different ways to create Pandas Dataframe Read Aloud allows you to select from a variety of text-to-speech voices, including those provided natively by the browser, as well as by text-to-speech cloud service providers such as Google.
Reading and Writing to text files in Python As you may guess, gTTS stands for Google Text To Speech, it is a Python library to interface with Google Translates text to speech API.
You will simply add to your language translation bot and invite this bot to chat in your chat window. I found on the figure that the English to French translation is en2fr. Step By Step Implementation We will be using the Google-Text-to-Speech i.e., gTTS() function of the gtts module for speaking the translated text into the. As an example, let’s translate from English to French. If Chat detects a language that is different than what is.
#GOOGLE TRANSLATE BOT TEXT TO SPEECH HOW TO#
Python program to convert a list to string How To Use The Translation Bot First, select the language you would like to have translated. When an end user clicks to start a new chat, Zendesk checks the first word and string of text.
How to get column names in Pandas dataframe TTS Voice presented by animated speaking characters will read the text in the most realistic, human-sounding way in English U.S., Chinese, French, German.
Adding new column to existing DataFrame in Pandas.
ISRO CS Syllabus for Scientist/Engineer Exam.
ISRO CS Original Papers and Official Keys.
GATE CS Original Papers and Official Keys.

1 note
·
View note
Text
Introductory To Knowledge Analysis Using Excel

After numerous hours and sessions of research and learning, we’ve narrowed down the record of one of the best Data Analytics coaching and online programs excellent for novices, intermediates and specialists alike. This list contains both free and paid online programs that will help you study data evaluation. In this information, we’ll present you what one of the best data analytics courses with certificates to study knowledge analysis are, and how one can get a few of these knowledge analytics training classes at no cost or for less.
If you are looking to improve your excel expertise THIS is the company you should invest your time in.
Excel, however most individuals don’t know fairly how advanced spreadsheet evaluation can get.
You'll additionally study how to identify the computing requirements appropriate for fixing those issues.
Initially, you'll study some foundational ideas, together with primary calculations such as imply, median, and commonplace deviation, and provides an introduction to the central limit theorem.
Start by learning key information analysis tools such as Microsoft Excel, Python, SQL and R.
On some stage, every business relies on information science in one way or one other. That’s why plenty of firms rent information analysts and knowledge scientists interchangeably. Smaller organizations often mix the role; which means knowledge analysts have to have a good suggestion of knowledge sciences. Data analysts gather, consider, and analyze raw knowledge to help corporations in their decision-making process. Ideally, information analysts gather data from a quantity of sources, together with direct and oblique sources, and carry out thorough information evaluation to communicate the relevant findings instantly or via well-designed stories. When you buy the course, you get free entry to their Data Fundamentals Handbook that features all the content of the course in written form.
Chance And Statistics In Information Science Using Python
Alison provides dozens of excessive quality knowledge science courses designed by specialists and universities to provide you with an interactive and enriched learning expertise. When joining any of those courses you want to make the same commitment to learning as you'll in the course of a school course. One goal for studying data science online is to maximize psychological discomfort. It’s easy to get caught in the behavior of signing in to look at a few videos and really feel like you’re learning, but you’re not likely studying much until it hurts your mind.
You will use Python's DataFrame a two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular information structure with labeled axes . To take this course, you must already be familiar with Python programming language; all code writing is in Jupyter notebooks. You will work with fundamental Pandas knowledge constructions, Pandas Series objects representing a single column of information which can retailer numerical values, strings, Booleans, and extra advanced knowledge varieties. Learn the means to use Pandas DataFrame, which represents data in table type. Finally, be taught to append and kind collection values, add lacking information, add columns, and combination information in a DataFrame. In this Skillsoft Aspire course, learners will encounter primary Hadoop file system operations similar to viewing the contents of directories and creating new ones. [newline]Begin by working with recordsdata in various ways, including transferring recordsdata between a local file system and HDFS and discover ways to create and delete information on HDFS.
What is the difference between data analytics and data analysis?
Data analysis refers to the process of examining, transforming and arranging a given data set in specific ways in order to study its individual parts and extract useful information. Data analytics is an overarching science or discipline that encompasses the complete management of data.
Every yr, 10 students will get suggestions on their project from information scientists working at Airbnb. At the tip of the course, college students complete a Capstone Project designed in conjunction with Yahoo. The entire Specialization takes about forty hours to complete, which means that students can finish the program in simply six months in the occasion that they spend three hours a week studying.
College Students Rated Our Data Analytics Lessons
Finally, observe how to create and analyze categories of information in a knowledge set by utilizing Windows. Extracting meaningful info from a really massive dataset could be painstaking. In this Skillsoft Aspire course, learners examine how Hadoop's MapReduce can be utilized to hurry up this operation.
Is data Analytics a stressful job?
Data analysis is a stressful job. Although there are multiple reasons, high on the list is the large volume of work, tight deadlines, and work requests from multiple sources and management levels.
New options, particular provides, and exciting information about the world of information visualization. Python is a high-level, dynamically typed, and transportable programming language that excels when the value of software development outweighs performance concerns. Data governance is an built-in framework of insurance policies and technology applied to ensure effective knowledge administration.
Unit 1: Introduction To Python
These sources embrace each free and paid ones created by top professionals, schools and corporations. There are 4 programs in the program – Foundations of strategic enterprise analytics, Foundations of promoting analytics, Case studies in enterprise analytics with Accenture and Capstone Project. Learners need to finish all the 4 programs to earn MicroMasters program certificates from ColumbiaX.
youtube
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP Deep Learning Interview Questions and Answers
Deep Learning Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Deep Learning? Deep learning is one part of a broader group of machine learning techniques based on learning data analytics designs, as exposed through task-specific algorithms. Deep Learning can be supervised us a semi-supervised or unsupervised. 2. Which data visualization libraries do you use and why they are useful? It is valuable to determine your views value on the data value properly visualization and your individual preferences when one comes to tools. Popular methods add R’s ggplot, Python’s seaborn including matplotlib value, and media such as Plot.ly and Tableau. 3. Where do you regularly source data-sets? This type of questions remains any real tie-breakers. If someone exists going into an interview, he/she need to remember this drill of any related question. That completely explains your interest in Machine Learning. 4. What is the cost function? A cost function is a strength of the efficiency of the neural network data-set value with respect to given sample value and expected output data-set. It is a single value of data-set-function, non-vector as it gives the appearance of the neural network as a whole. MSE=1nΣi=0n(Y^i–Yi)^2 5. What are the benefits of mini-batch gradient descent? This is more efficient of compared tools to stochastic gradient reduction. The generalization data value by determining the flat minima. The Mini-batches provides help to approximate the gradient of this entire data-set advantage which helps us to neglect local minima. 6. What is mean by gradient descent? Gradient descent defined as an essential optimization algorithm value point, which is managed to get the value of parameters that reduces the cost function. It is an iterative algorithm data value function which is moves towards the direction of steepest data value function relationship as described by the form of the gradient. Θ: =Θ–αd∂ΘJ(Θ) 7. What is meant by a backpropagation? It ‘s Forward to the propagation of data-set value function in order to display the output data value function. Then using objective value also output value error derivative package is computed including respect to output activation. Then we after propagate to computing derivative of the error with regard to output activation value function and the previous and continue data value function this for all the hidden layers. Using previously calculated the data-set value and its derivatives the for output including any hidden stories we estimate error derivatives including respect to weights. 8. What is means by convex hull? The convex hull is represents to the outer boundaries of the two-level group of the data point. Once is the convex hull has to been created the data-set value, we get maximum data-set value level of margin hyperplane (MMH), which attempts to create data set value the greatest departure between two groups data set value, as a vertical bisector between two convex hulls data set value. 9. Do you have experience including Spark about big data tools for machine learning? The Spark and big data mean most favorite demand now, able to the handle high-level data-sets value and including speed. Be true if you don’t should experience including those tools needed, but more take a look into assignment descriptions also understand methods pop. 10. How will do handle the missing data? One can find out the missing data and then a data-set value either drop thorugh those rows value or columns value or decide value to restore them with another value. In python library using towards the Pandas, there are two thinging useful functions helpful, IsNull() and drop() the value function.

Deep Learning Interview Questions 11. What is means by auto-encoder? An Auto-encoder does an autonomous Machine learning algorithm data that uses backpropagation system, where that target large values are data-set to be similar to the inputs provided data-set value. Internally, it converts a deep layer that describes a code used to represent specific input. 12. Explain about from Machine Learning in industry. Robots are replacing individuals in various areas. It is because robots are added so that all can perform this task based on the data-set value function they find from sensors. They see from this data also behaves intelligently. 13. What are the difference Algorithm techniques in Machine Learning? Reinforcement Learning Supervised Learning Unsupervised Learning Semi-supervised Learning Transduction Learning to Learn 14. Difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning? Supervised learning is a method anywhere that requires instruction defined data While Unsupervised learning it doesn’t need data labeling. 15. What is the advantage of Naive Bayes? The classifier preference converge active than discriminative types It cannot learn that exchanges between characteristics 16. What are the function using Supervised Learning? Classifications Speech recognition Regression Predict time series Annotate strings 17. What are the functions using Unsupervised Learning? To Find that the data of the cluster of the data To Find the low-dimensional representations value of the data To Find determine interesting with directions in data To Find the Magnetic coordinates including correlations To Find novel observations 18. How do you understanding Machine Learning Concepts? Machine learning is the use of artificial intelligence that provides operations that ability to automatically detect further improve from occurrence without doing explicitly entered. Machine learning centers on the evolution of network programs that can access data and utilize it to learn for themselves. 19. What are the roles of activation function? The activation function means related to data enter non-linearity within the neural network helping it to learn more system function. Without which that neural network data value would be simply able to get a linear function which is a direct organization of its input data. 20. Definition of Boltzmann Machine? Boltzmann Machine is used to optimize the resolution of a problem. The work of the Boltzmann machine is essential to optimize data-set value that weights and the quantity for data Value. It uses a recurrent structure data value. If we apply affected annealing on discrete Hopfield network, when it would display Boltzmann Machine. Get Deep Learning 100% Practical Training 21. What is Overfitting in Machine Learning? Overfitting in Machine Learning is described as during a statistical data model represents random value error or noise preferably of any underlying relationship or when a pattern is extremely complex. 22. How can you avoid overfitting? Lots of data Cross-validation 23. What are the conditions when Overfitting happens? One of the important design and chance of overfitting is because the models used as training that model is the same as that criterion used to assess the efficacy of a model. 24. What are the advantages of decision trees? The Decision trees are easy to interpret Nonparametric There are comparatively few parameters to tune 25. What are the three stages to build the hypotheses or model in machine learning? Model building Model testing Applying the model 26. What are parametric models and Non-Parametric models? Parametric models remain these with a limited number from parameters also to predict new data, you only need to understand that parameters from the model. Non Parametric designs are those with an unlimited number from parameters, allowing to and flexibility and to predict new data, you want to understand the parameters of this model also the state from the data that has been observed. 27. What are some different cases uses of machine learning algorithms can be used? Fraud Detection Face detection Natural language processing Market Segmentation Text Categorization Bioinformatics 28. What are the popular algorithms for Machine Learning? Decision Trees Probabilistic networks Nearest Neighbor Support vector machines Neural Networks 29. Define univariate multivariate and bivariate analysis? if an analysis involves only one variable it is called as a univariate analysis for eg: Pie chart, Histogram etc. If a analysis involves 2 variables it is called as bivariate analysis for example to see how age vs population is varying we can plot a scatter plot. A multivariate analysis involves more than two variables, for example in regression analysis we see the effect of variables on the response variable 30. How does missing value imputation lead to selection bias? Case treatment- Deleting the entire row for one missing value in a specific column, Implutaion by mean: distribution might get biased for instance std dev, regression, correlation. 31. What is bootstrap sampling? create resampled data from empirical data known as bootstrap replicates. 32. What is permutation sampling? Also known as randomization tests, the process of testing a statistic based on reshuffling the data labels to see the difference between two samples. 33. What is total sum of squares? summation of squares of difference of individual points from the population mean. 34. What is sum of squares within? summation of squares of difference of individual points from the group mean. 35. What is sum of squares between? summation of squares of difference of individual group means from the population mean for each data point. 36. What is p value? p value is the worst case probability of a statistic under the assumption of null hypothesis being true. 37. What is R^2 value? It’s measures the goodness of fit for a linear regression model. 38. What does it mean to have a high R^2 value? the statistic measures variance percentage in dependent variable that can be explained by the independent variables together. 40. What are residuals in a regression model? Residuals in a regression model is the difference between the actual observation and its distance from the predicted value from a regression model. 41. What are fitted values, calculate fitted value for Y=7X+8, when X =5? Response of the model when predictors values are used in the model, Ans=42. 42. What pattern should residual vs fitted plots show in a regression analysis? No pattern, if the plot shows a pattern regression coefficients cannot be trusted. 43. What is overfitting and underfitting? overfitting occurs when a model is excessively complex and cannot generalize well, a overfitted model has a poor predictive performance. Underfitting of a model occurs when the model is not able to capture any trends from the data. 44. Define precision and recall? Recall = True Positives/(True Positives + False Negatives), Precision = True Positives/(True Positives + False Positive). 45. What is type 1 and type 2 errors? False positives are termed as Type 1 error, False negative are termed as Type 2 error. 46. What is ensemble learning? The art of combining multiple learning algorithms and achieve a model with a higher predictive power, for example bagging, boosting. 47. What is the difference between supervised and unsupervised machine learning algorithms? In supervised learning we use the dataset which is labelled and try and learn from that data, unsupervised modeling involves data which is not labelled. 48. What is named entity recognition? It is identifying, understanding textual data to answer certain question like “who, when,where,What etc.” 49. What is tf-idf? It is the measure if a weight of a term in text data used majorly in text mining. It signifies how important a word is to a document. tf -> term frequency – (Count of text appearing in the data) idf -> inverse document frequency tfidf -> tf * idf 50. What is the difference between regression and deep neural networks, is regression better than neural networks? In some applications neural networks would fit better than regression it usually happens when there are non linearity involved, on the contrary a linear regression model would have less parameters to estimate than a neural network for the same set of input variables. thus for optimization neural network would need a more data in order to get better generalization and nonlinear association. 51. How are node values calculated in a feed forward neural network? The weights are multiplied with node/input values and are summed up to generate the next successive node 52. Name two activation functions used in deep neural networks? Sigmoid, softmax, relu, leaky relu, tanh. 53. What is the use of activation functions in neural networks? Activation functions are used to explain the non linearity present in the data. 54. How are the weights calculated which determine interactions in neural networks? The training model sets weights to optimize predictive accuracy. 55. which layer in a deep learning model would capture a more complex or higher order interaction? The last layer. 56. What is gradient descent? It comprises of minimizing a loss function to find the optimal weights for a neural network. 57. Imagine a loss function vs weights plot depicting a gradient descent. At What point of the curve would we achieve optimal weights? local minima. 58. How does slope of tangent to the curve of loss function vs weigts help us in getting optimal weights for a neural network Slope of a curve at any point will give us the direction component which would help us decide which direction we would want to go i.e What weights to consider to achieve a less magnitude for loss function. 59. What is learning rate in gradient descent? A value depicting how slowly we should move towards achieving optimal weights, weights are changedby the subtracting the value obtained from the product of learning rate and slope. 60. If in backward propagation you have gone through 9 iterations of calculating slopes and updated the weights simultaneously, how many times you must have done forward propagation? 9 61. How does ReLU activation function works? Define its value for -5 and +7 For all x>=0, the output is x, for all x Read the full article
0 notes
Text
Merge Excel Files In Python

How to move data from one Excel file to another using Python The Use Case. We have an Excel workbook that contains 2019 reported sales for 28 stores across the US. Step 1 — Import the Pandas library. I will open Visual Studio Code and create a new file. I will save that file as. Merge Two Files in Python. To merge two files in python, you have to ask from user to enter name of the first and second file, and then ask a file name to create a file to place the merged content of the two file into this newly created file.
Merge Excel Files In Python Free
Python Read Multiple Excel Files
EasyXLS Excel library can be used to export Excel files with Python on Windows, Linux, Mac or other operating systems. The integration vary depending on the operating system or if the bridge for .NET Framework of Java is chosen:
1. EasyXLS on Windows using .NET Framework with Python
2. EasyXLS on Linux, Mac, Windows using Java with Python
EasyXLS on Windows using .NET Framework with Python
If you opt for the .NET version of EasyXLS, the below code requires Pythonnet, a bridge between Python and .NET Framework.
Step 1: Download and install EasyXLS Excel Library for .NET
To download the trial version of EasyXLS Excel Library, press the below button:
If you already own a license key, you may login and download EasyXLS from your account.
Step 2: Install Pythonnet
For the installation you need to run 'pip' command as it follows. Pip is a package-management system used to install and manage software packages written in Python. <Python installation path>Scripts>pip install 'pythonnet.whl'
Step 3: Include EasyXLS library into project
EasyXLS.dll must be added to your project. EasyXLS.dll can be found after installing EasyXLS, in 'Dot NET version' folder.
Step 4: Run Python code that merges cells in Excel sheet
Execute the following Python code that exports an Excel file with merge cells.
EasyXLS on Linux, Mac, Windows using Java with Python
If you opt for the Java version of EasyXLS, a similar code as above requires Py4J, Pyjnius or any other bridge between Python and Java.
Step 1: Download and install EasyXLS Excel Library for Java
To download the trial version of EasyXLS Excel Library, press the below button:
If you already own a license key, you may login and download EasyXLS from your account.
Step 2: Install Py4j
For the Py4j installation you need to run 'pip' command as it follows. Pip is a package-management system used to install and manage software packages written in Python. <Python installation path>Scripts>pip install 'py4j.whl'
Step 3: Create additional Java program
The following Java code needs to be running in the background prior to executing the Python code.
Step 4: Add py4j library to CLASSPATH
py4j.jar must be added to your classpath of the additional Java program. py4j.jar can be found after installing Py4j, in '<Python installation path>sharepy4j' folder.
Step 5: Add EasyXLS library to CLASSPATH
EasyXLS.jar must be added to your classpath of the additional Java program. EasyXLS.jar can be found after installing EasyXLS, in 'Lib' folder.
Step 6: Run additional Java program
Start the gateway server application and it will implicitly start Java Virtual Machine as well.
Step 7: Run Python code that merges cells in Excel sheet
Execute a code as below Python code that exports an Excel file with merge cells.
Related sections
See also
How to format Excel cells?
How to export to XLSX file?
How to export to XLSM file?
How to export to XLSB file?
How to export to XLS file?
Related methods
ExcelTable.easy_mergeCells ExcelTable.easy_removeCellMerging ExcelTable.MergeCellRangesCount ExcelTable.easy_getCellMergingFirstRow ExcelTable.easy_getCellMergingFirstCol ExcelTable.easy_getCellMergingLastRow ExcelTable.easy_getCellMergingLastCol
Withthe help of openpyxl module we can also write to excel file in python.The process is somewhat similar to reading an excel spreadsheet inpython. With python Excel writer, we will Create excel sheets, write text, numbers and formula in cells. After modifying we will save workbook. We will also add and delete sheets in a an excel workbook, apply setting, fonts and styles, set width and height of cells and areas, merge and unmerge cells. We can create any type of excel file, having hundredsand thousands of columns and rows of data. Writing to excel files is anecessity which no one can deny. There may be many cases for allprofessionals from a computer operator to a data scientist that one hasto write to an excel spreadsheet in python. Here is the solution.
If you want to Read, Write and Manipulate(Copy, cut, paste, delete or search for an item etc) Excel files in Python with simple and practical examples I will suggest you to see this simple and to the point Excel Openpyxl Course with examples about how to deal with MS Excel files in Python. This video course teaches efficiently how to manipulate excel files and automate tasks.
Everything you do in Microsoft Excel, can be automated with Python. So why not use the power of Python and make your life easy. You can make intelligent and thinking Excel sheets, bringing the power of logic and thinking of Python to Excel which is usually static, hence bringing flexibility in Excel and a number of opportunities.
Python Excel Create and Save files:
First we will learn how to create and save excel files with python.First we will create an excel file.
First step will be to import openpyxlmodule.
>>> import openpyxl
Next we will create an excel file ortechnically a Workbook.
>>> mywb =openpyxl.Workbook()
The above code will create a work book with one sheet in the beginning.We can check the number of sheets with the following code, see whichsheet is active and what is the title of the active sheet. In this casewe have only one sheet, hence it will be the only answer.
>>>mywb.get_sheet_names()
('Sheet')
>>> sheet =mywb.active
>>> sheet.title
Check out the latest NASA news for up-to-date information on the ISS. Amateur Radio on the International Space Station is a program that lets students experience the excitement of Amateur Radio by talking directly with crew members of the International Space Station. Get the latest news, images, videos and more from humanity's home in orbit - the International Space Station. NASA.gov brings you the latest images, videos and news from America's space agency. Get the latest updates on NASA missions, watch NASA TV live, and learn about our quest to reveal the unknown and benefit all humankind. Iss astronauts. WHO IS IN SPACE is a project created by Destin Sandlin of Smarter Every Day. The goal of this project is to spread the amazing actions, feats and words of the men and women currently aboard the International Space Station.
'Sheet'
We can also set the title of thesheet, see the example given below.
>>>sheet.title = 'MyNewTitle'
>>>wb.get_sheet_names()
('MyNewTitle')
>>>mywb.save('NewExcelFile.xlsx')
If you open your root folder orcurrent working directory, you will find a new excel file, with nameNewExcelFile, having one sheet with title MyNewTitle.
Loading an already existing excel file in Python and saving acopy of it:
Whenever you load an already existing Excel file in memory, and modifythe contents, either sheets or cells, or creating whole sheets, ordeleting sheets, or any modification which could be done, you will haveto call save( ) method to save the file. If you don't do so, anymodification will be lost.
>>> import openpyxl
>>>mywb = openpyxl.load_workbook('filetest.xlsx')
>>>sheet = mywb.active
>>>sheet.title = 'Working on Save as'
>>>mywb.save('example_filetest.xlsx')
In the code above you noticed that weloaded already existing file, changed sheet title and saved its copywith a different name. In this case original file plus this new filewill be in your working directory, which is usually your python rootfolder. Open it and see the new copy.
When you work on an excel spreadsheetin python, its always better to save it with a different file name, sothat the original is always there, in case any mishap happens, forexample any bug in code, or mistake in saving, or writing.
Creating and Removing Sheets in Excel:
For creating new sheets in aworkbook, we use create_sheet( ) method.
For deleting a sheet we useremove_sheet( ) method.
>>>importopenpyxl
>>> mywb =openpyxl.Workbook()
>>> mywb.get_sheet_names()
('Sheet')
>>>mywb.create_sheet()
<Worksheet 'Sheet1'>
>>> mywb.get_sheet_names()
('Sheet', 'Sheet1')
>>>wb.create_sheet(index=0,)
<Worksheet '1st Sheet'>
>>>mywb.get_sheet_names()
('1st Sheet', 'Sheet', 'Sheet1')
>>>mywb.create_sheet(index=2,title='2ndSheet')
<Worksheet '2nd Sheet'>
>>>mywb.get_sheet_names()
('1st Sheet', 'Sheet', '2nd Sheet','Sheet1')
Create sheet creates a new sheet,which is by default the last sheet in the workbook. However, we canspecify the position of the new sheet with index number and we can alsopass a string as the title of new sheet. Keep in mind, the first sheetwill have index 0, second will have index 1 and so on.
Removing sheets from Excel Workbook:
When we want to remove any specificsheet from an excel workbook, we will use method remove_sheet( )
>>>mywb.get_sheet_names()
('1st Sheet', 'Sheet', '2nd Sheet','Sheet1')
This is to see the number of sheets and their names, now working withremoving or deleting sheets.
>>>mywb.remove_sheet(mywb.get_sheet_by_name('1st Sheet'))
>>>mywb.remove_sheet(mywb.get_sheet_by_name('Sheet1'))
>>>mywb.get_sheet_names()
('Sheet', '2nd Sheet')
It is very obvious that afterdeleting the two sheets from four sheets, only two sheets are left.remove_sheet method takes a worksheet object not name of the sheet,instead of creating an object to that specific worksheet and thenremoving it, we call get_sheet_by_name( ) and pass it the name ofsheet, the value it returns is the input argument of remove_sheet( )method. In the end, use save( ) method to save the file aftermodification. In this case removal of worksheets.
Python excel Writing Values in Cells:
Now we will see how to write valuesto particular cells in an excel worksheet. Ofcourse we should know theaddress of the cell where we want to write.
>>> import openpyxl
>>> mywb =openpyxl.Workbook()
>>> mysheet =mywb.get_sheet_by_name('Sheet')
>>> mysheet('F6') ='Writing new Value!'
>>> mysheet('F6').value
'Writing new Value'
Python Excel setting Fonts:
Applying different styles to yoursheet, emphasizes or stresses certain rows or columns. It is veryimportant to apply certain uniform styles to your excel sheets so thatit brings clarity in reading the data. If you have hundreds orthousands of rows of data, styling can be a hectic job, however, withour python code, you can write a few lines of code and apply onmillions of lines of data instantly. But take care, first stylingshould be with absolute care, and second always save excel workbookwith a different name.
First we will import openpyxl, and then import Font and Style for usein our code.
Here’s an example that creates a newworkbook and sets cell F6 to have a 32-point, italicized font.
>>>importopenpyxl
>>>fromopenpyxl.styles import Font, Style
>>>mywb= openpyxl.Workbook()
>>>mysheet= mywb.get_sheet_by_name('Sheet')
>>>italic32Font = Font(size=32, italic=True)
>>>sobj = Style(font=italic24Font)
>>>mysheet('F6').style = sobj
>>>mysheet('F6')= 'Applying Styles!'
>>>mywb.save('Appliedstyle.xlsx')
In openpyxl for excel worksheets eachcell has a style object which is in style attribute of the cell. Wecreate a style object and assign it to style attribute.
There are four arguments for Font objects
Name: A string value is used, quoting the font name, like'Arial'.
Size: An integer value, quoting the size.
Bold: A boolean value, True for Bold font.
Italic: Boolean value, True for Italic font.
In the example below we will call Font( ) method to create a Fontobject and store it in a variable, next step will be to pass that as anargument to Style( ) method. We will store the that object in anothervariable and assign it to the specific cell object.
>>> import openpyxl
>>> fromopenpyxl.styles import Font, Style
>>> mywb =openpyxl.Workbook()
>>> mysheet =mywb.get_sheet_by_name('Sheet')
>>> firstFontObj =Font(name='Arial',bold=True)
>>> firstStyleObj =Style(font=firstFontObj)
>>>mysheet('F6').style/firstStyleObj
>>> mysheet('F6') ='Bold Arial'
>>> secondFontObj =Font(size=32, italic=True)
>>> secondStyleObj =Style(font=secondFontObj)
>>>mysheet('D7').style/secondStyleObj
>>> mysheet('D7') ='32 pt Italic'
>>>mywb.save('ApplicationofStyles.xlsx')
Python ExcelWriting Formulae:
Formulae in Excel are very important, infact the power of a spreadsheetis in its formulae. Openpyxl provides the utility of writing formula inany specific cell. Infact it is very much easy, instead of writing anumber or text, write an equal sign followed by the required formula. >>>mysheet('F6')= '=Sum(D7:D20)'
This formula will sum up all valuesfrom D7 to D20 and store in F6 cell.
Some more examples:
>>> import openpyxl
>>> mywb =openpyxl.Workbook()
>>> mysheet =mywb.active
>>> mysheet('F6') =500
>>> mysheet('F7') =800
>>> sheet('D3') ='=SUM(F6:F7)'
>>>mywb.save('Applyingformula.xlsx')
In the above example we put 500 inF6, and 800 in F7 cell. Cell D3 has a formula of adding up F6 and F7.When you will open spreadsheet, it will show a value of 1300 in D3.
The cells in A1 and A2 are set to 200and 300, respectively.The value in cell A3 is set to a formula that sums the values in A1 andA2.When the spreadsheet is opened in Excel, A3 will display its value as500.
Excel Adjusting Rows and Columns in a Sheet:
We can set Row heigh, column width in excel spreadsheet using openpyxl.We can also freeze rows or columns so that they always appear. We canalso hide rows or columns.
>>> import openpyxl
>>> mywb =openpyxl.Workbook()
>>> mysheet =mywb.active
>>> mysheet('F6') ='Tall row'
>>> mysheet('D7') ='Wide column'
>>> mysheet.row_dimensions(3).height= 65
>>>mysheet.column_dimensions('F').width= 25
>>>mywb.save('Heightandwidth.xlsx')
Thedefault row height in excel spreadsheet is 12.75 points. Where onepoint is equal to 1/72 of an inch. You can set a value between 0 to 409. Column width can be set to a value from 0 to 255. It can be either aninteger or a floating value (decimal number). If you set 0 width forcolumn or 0 height for rows, it will be hidden.
Excel Merging and unmerging
openpyxl allows us to merge andunmerge cells in a workbook.
>>> import openpyxl
>>>my wb =openpyxl.Workbook()
>>> mysheet =mywb.active
>>>mysheet.merge_cells('B2:D3')
>>> mysheet('A1') ='cells mergedtogether.'
>>> mysheet.merge_cells('F6:F7')
>>> mysheet('G5') ='Two merged cells.'
>>> mywb.save('Mergingcells.xlsx')
merge_cells method takes two celladdresses as its arguments. First cell is the top left and second cellis the right bottom of the rectangular area that is to be merged. If wewant to set value of that merged area, we use the address of top leftcell of the whole merged area.
If you want to unmerge cells, use theidea below.
>>> import openpyxl
>>> mywb =openpyxl.load_workbook('Mergingcells.xlsx')
>>> mysheet =mywb.active
>>>mysheet.unmerge_cells('B2:D3')
>>> mysheet.unmerge_cells('F6:F7')
Merge Excel Files In Python Free
Retroarch on chromebook app. >>> mywb.save('unmerged.xlsx')
If you want to Read, Write and Manipulate(Copy, cut, paste, delete or search for an item etc) Excel files in Python with simple and practical examples I will suggest you to see this simple and to the point Excel Openpyxl Course with examples about how to deal with MS Excel files in Python. This video course teaches efficiently how to manipulate excel files and automate tasks.
Python Read Multiple Excel Files
Everything you do in Microsoft Excel, can be automated with Python. So why not use the power of Python and make your life easy. You can make intelligent and thinking Excel sheets, bringing the power of logic and thinking of Python to Excel which is usually static, hence bringing flexibility in Excel and a number of opportunities.

0 notes
Text
Basic Data Analysis with MySQL Shell Python mode
I recently watched a fantastic Python Pandas library tutorial series on YouTube. Without a doubt, Pandas is great for all sorts of data stuff. On the same token, MySQL Shell in Python mode is quite powerful in the sense that Python and the MySQL Shell (version >= 8.0) are somewhat united in the same environment. Although Pandas is in a league all its own when it comes to data analysis, between the power of MySQL and Python, we can also perform some basic analysis easily in MySQL Shell Python mode. In this blog post, I will cover some basic data analysis using Python mode in the MySQL Shell. Continue reading to see examples… Business vector created by freepik – www.freepik.com OS, Software, and DB used: OpenSuse Leap 15.1 MySQL 8.0.21 Self-Promotion: If you enjoy the content written here, by all means, share this blog and your favorite post(s) with others who may benefit from or like it as well. Since coffee is my favorite drink, you can even buy me one if you would like! Data Set Used You can download the Stack Overflow Developer Survey Results data set used in this post for your own exploration if you would like. Basic Data Analysis with MySQL Shell Python Mode: Connecting, table row and column count, column names For starters, we use the available global db object and get a connection to an existing table in the database/schema by passing in a name to the get_table() method: 1 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data = db.get_table('so_data') I store the ‘so_data’ table in a shell.Object variable named ‘data’. We can call the count() method against this object and get a count of the total rows in the table: 12 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data.count()88883 Related: Read the post, Dynamic MySQL CREATE TABLE statement with pandas and pyodbc, I wrote and see how I dynamically created the ‘so_data’ table and populated it with accompanying data. Calling the select() method on the ‘data’ object, I can essentially retrieve all rows and columns from the table. However, at this time, I am only interested in the actual column names of the table. I’ll store this result in a ‘rows’ object variable: 1 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > rows = data.select().execute() With the ‘rows’ variable, I call the get_column_names() method on it and am returned a Python list of all the table’s column names: 12345678910111213 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > cols = rows.get_column_names() MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > cols[ "Respondent", "MainBranch", "Hobbyist", "OpenSourcer", "OpenSource", "Employment", "Country", "Student", "EdLevel", "UndergradMajor", "EduOther", "OrgSize", "DevType", "YearsCode", "Age1stCode", "YearsCodePro", "CareerSat", "JobSat", "MgrIdiot", "MgrMoney", "MgrWant", "JobSeek", "LastHireDate", "LastInt", "FizzBuzz", "JobFactors", "ResumeUpdate", "CurrencySymbol", "CurrencyDesc", "CompTotal", "CompFreq", "ConvertedComp", "WorkWeekHrs", "WorkPlan", "WorkChallenge", "WorkRemote", "WorkLoc", "ImpSyn", "CodeRev", "CodeRevHrs", "UnitTests", "PurchaseHow", "PurchaseWhat", "LanguageWorkedWith", "LanguageDesireNextYear", "DatabaseWorkedWith","DatabaseDesireNextYear", "PlatformWorkedWith", "PlatformDesireNextYear", "WebFrameWorkedWith", "WebFrameDesireNextYear", "MiscTechWorkedWith", "MiscTechDesireNextYear", "DevEnviron", "OpSys", "Containers", "BlockchainOrg", "BlockchainIs", "BetterLife", "ITperson", "OffOn", "SocialMedia", "Extraversion", "ScreenName", "SOVisit1st", "SOVisitFreq", "SOVisitTo", "SOFindAnswer", "SOTimeSaved", "SOHowMuchTime", "SOAccount", "SOPartFreq", "SOJobs", "EntTeams", "SOComm", "WelcomeChange", "SONewContent", "Age", "Gender", "Trans", "Sexuality", "Ethnicity", "Dependents", "SurveyLength", "SurveyEase"] As you can see, there are quite a lot of columns in this table. Instead of counting them myself, I use the Python len() method and get a count of the ‘cols’ list object: 12 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > len(cols)85 Summary: We can use combinations of MySQL Shell methods: get_table(), count(), select(), get_column_names() and the Python len() method and determine pertinent table meta-data information. Basic Data Analysis with MySQL Shell Python Mode: Select specific columns, distinct/unique column values, and constraining rows We learned in the previous section that table ‘so_data’ has over 80k rows of data, along with 85 total columns. That alone is nothing to scoff at. Instead of loading up our screens with many many rows and columns, I’ll utilize several of the available MySQL Shell methods, choosing certain columns and constraining the number of returned rows (if any). The select() method can accept a list of columns names, separated by commas. In this next query, I specify just the ‘SocialMedia’ column and limit the total number of rows to 10, using the limit() method: 12345678910111213141516 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data.select('SocialMedia').limit(10).execute()+-------------+| SocialMedia |+-------------+| Twitter || Instagram || Reddit || Reddit || Facebook || YouTube || YouTube || YouTube || Twitter || YouTube |+-------------+10 rows in set (0.0010 sec) Pro Tip: The limit() method parameter is the number of rows you want to be returned from theselect() method. While the above query does provide good information, suppose we need to know of all the unique values in the ‘SocialMedia’ column. We can easily include the DISTINCT keyword in the call to select() with the desired column name: 123456789101112131415161718192021 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data.select('DISTINCT (SocialMedia)').execute()+--------------------------+| SocialMedia |+--------------------------+| Twitter || Instagram || Reddit || Facebook || YouTube || NA || VK ВКонта́кте || WhatsApp || I don''t use social media|| WeChat || LinkedIn || Snapchat || Weibo || Hello || Youku Tudou |+--------------------------+15 rows in set (0.2199 sec) Based on the returned query results, we can see there are 15 unique values for the ‘SocialMedia’ column. Summary: The select() method is capable of choosing either all table columns or individual columns depending on your needs and the column names supplied as parameters. If you need specific columns in your query results, provide those columns separated by commas as parameters to select(). select() also allows MySQL keywords to be included with columns should you need any of them as in the example query using DISTINCT. On the other hand, constrain the number of output rows returned from any query using the limit() method by specifying the number of desired rows using limit()‘s number parameter. Basic Data Analysis with MySQL Shell Python Mode: Counting, group by, and other aggregate functions In the previous section, we executed a query using select() and DISTINCT, retrieving the unique values in the ‘SocialMedia’ column. We have these results from that query: 123456789101112131415161718192021 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data.select('DISTINCT (SocialMedia)').execute()+--------------------------+| SocialMedia |+--------------------------+| Twitter || Instagram || Reddit || Facebook || YouTube || NA || VK ВКонта́кте || WhatsApp || I don''t use social media|| WeChat || LinkedIn || Snapchat || Weibo || Hello || Youku Tudou |+--------------------------+15 rows in set (0.2199 sec) What is the total number of non-NULL rows for each unique ‘SocialMedia’ column value in the ‘so_data’ table? Can we find out with MySQL Shell Python mode? Absolutely. We can use the COUNT() aggregate function on the ‘SocialMedia’ column right in the select() method. However, we need a GROUP BY clause in the query as well. MySQL Shell has us covered with a same-named method, group_by(). In this query, I’ll retrieve a count of the actual values in the ‘SocialMedia’ column (ignoring NULL‘s in that count) and group those counts by the ‘SocialMedia’ column: 123456789101112131415161718192021 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data.select('SocialMedia', 'COUNT(SocialMedia) AS num_medias').group_by('SocialMedia').execute()+--------------------------+------------+| SocialMedia | num_medias |+--------------------------+------------+| Twitter | 11398 || Instagram | 6261 || Reddit | 14374 || Facebook | 13178 || YouTube | 13830 || NA | 4446 || VK ВКонта́кте | 603 || WhatsApp | 13347 || I don''t use social media| 5554 || WeChat | 667 || LinkedIn | 4501 || Snapchat | 628 || Weibo | 56 || Hello | 19 || Youku Tudou | 21 |+--------------------------+------------+15 rows in set (0.2566 sec) Summary: We can easily query using aggregate functions in the select() method and group on appropriate columns with the group_by() method. Basic Data Analysis with MySQL Shell Python Mode: Filter rows with where and bind query criteria values The WHERE clause is responsible for filtering out which rows are returned from a query by way of some predicate test. Without a WHERE clause, all rows are returned from a SELECT query. Maybe you want that. Maybe not. If not, use WHERE to filter rows according to your needs. The WHERE clause is not limited to only the SELECT statement, as it is highly important in the DML commands UPDATE and DELETE. Without a WHERE clause targeting a specific row or rows, all rows are affected – in the case of DML (UPDATE and DELETE) – or returned from a SELECT query. MySQL Shell has a where() method we can use to filter the rows in a select() query just the same as in regular MySQL (or any SQL dialect). It is generally a good practice not to include potential user input values into our query expressions. Most programming languages have some sort of binding mechanism in place that imposes a sort of parameterized query and/or a prepared statement. Using parameterized queries and prepared statements, we can greatly reduce the risk of SQL Injection attacks. MySQL Shell has a bind() method we can use instead of directly concatenating values into the query strings of the where() predicate test(s). bind() accepts named parameters (which is what I will use in the examples below) or the universal ‘?’ style of parameter binding. Readers may be interested in the ‘DatabaseWorkedWith’ column of the ‘so_data’ table so let’s filter that column by rows where the ‘SocialMedia’ column is ‘Hello’ using where() and bind(): 1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > qry_cols = 'DatabaseWorkedWith' MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data.select(qry_cols).where('SocialMedia = :soc_media').bind('soc_media', 'Hello').execute()+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| DatabaseWorkedWith |+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| Microsoft SQL Server;MySQL;SQLite || Cassandra || MySQL;Redis || Microsoft SQL Server;MySQL || NA || NA || Cassandra;Elasticsearch;Microsoft SQL Server;Oracle;SQLite || PostgreSQL || Cassandra || NA || NA || DynamoDB || Cassandra || MongoDB;MySQL;Oracle;Other(s): || SQLite || NA || NA || NA || Cassandra;Couchbase;DynamoDB;Elasticsearch;Firebase;MariaDB;MongoDB;Microsoft SQL Server;MySQL;Oracle;PostgreSQL;Redis;SQLite;Other(s): |+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+19 rows in set (0.3925 sec) In this query, I use bind() and include a matching named placeholder (minus the colon : prefix) and corresponding value for what is specified in the where() method predicate. For example, in the where() method I used the ‘:soc_media’ named parameter and represented it in bind() with ‘soc_media’ and the actual accompanying value, ‘Hello’. Pretty straightforward. Oftentimes, you need to filter a SELECT query by more than one column or expression using multiple predicates. The MySQL Shell where() method easily accepts multiple predicate conditions just as a regular MySQL WHERE clause would using the AND and OR logical operators. But, with multiple where() predicates, that also means multiple parameterized values right? Yes, it does. However, multiple calls to bind() can be chained one after another, for each of the needed bound values. See the following query for a better understanding: 123456789101112131415161718 MySQL localhost:33060+ ssl learning Py > data.select(qry_cols).where('SocialMedia = :soc_media AND DatabaseWorkedWith <> :na').bind('soc_media', 'Hello').bind('na', 'NA').execute()+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| DatabaseWorkedWith |+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| Microsoft SQL Server;MySQL;SQLite || Cassandra || MySQL;Redis || Microsoft SQL Server;MySQL || Cassandra;Elasticsearch;Microsoft SQL Server;Oracle;SQLite || PostgreSQL || Cassandra || DynamoDB || Cassandra || MongoDB;MySQL;Oracle;Other(s): || SQLite || Cassandra;Couchbase;DynamoDB;Elasticsearch;Firebase;MariaDB;MongoDB;Microsoft SQL Server;MySQL;Oracle;PostgreSQL;Redis;SQLite;Other(s): |+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+12 rows in set (0.3308 sec) In the above query, we filtered using where() on columns ‘SocialMedia’ and ‘DatabaseWorkedWith’. For each of the columns, we also include a separate call to bind(). The first bind() method call includes the value ‘Hello’ for the ‘SocialMedia’ column named parameter ‘:soc_media’ and the second bind() method call has the matching parameters for the ‘DatabaseWorkedWith’ with column and the ‘NA’ value for the ‘:na’ placeholder. Summary: MySQL Shell provides powerful where() and bind() methods for row-filtering needs. Be sure and check out, X DevAPI User Guide for MySQL Shell in Python Mode, for in-depth information on many of the topics covered in today’s post along with much much more. Additional MySQL Shell Python mode articles you should read I have written several blog posts about MySQL Shell Python mode so feel free to check any of those that interest you: MySQL Shell CRUD With Python: Delete – with examples ALTER TABLE ADD COLUMN – MySQL Shell Python style MySQL Shell Python mode for multiple ALTER TABLE statements – easily Exploring .count() and COUNT() – MySQL Shell Python mode Column meta-data in MySQL Shell with Python mode MySQL Shell CRUD with Python: Read – with examples Transaction in MySQL Shell – Python mode with examples CREATE TABLE using Python in the MySQL Shell – with examples. MySQL Shell CRUD with Python: Create – with examples. MySQL Shell CRUD With Python: Update – with examples MySQL Shell Python mode is jam-packed with a ton of goodies and features. It opens up new options for working with data in the MySQL ecosystem. If you have not tried MySQL in Python mode, give it a shot. I am quite sure you will really like what you see. Like what you have read? See anything incorrect? Please comment below and thanks for reading!!! A Call To Action! Thank you for taking the time to read this post. I truly hope you discovered something interesting and enlightening. Please share your findings here, with someone else you know who would get the same value out of it as well. Visit the Portfolio-Projects page to see blog post/technical writing I have completed for clients. To receive email notifications (Never Spam) from this blog (“Digital Owl’s Prose”) for the latest blog posts as they are published, please subscribe (of your own volition) by clicking the ‘Click To Subscribe!’ button in the sidebar on the homepage! (Feel free at any time to review the Digital Owl’s Prose Privacy Policy Page for any questions you may have about: email updates, opt-in, opt-out, contact forms, etc…) Be sure and visit the “Best Of” page for a collection of my best blog posts. Josh Otwell has a passion to study and grow as a SQL Developer and blogger. Other favorite activities find him with his nose buried in a good book, article, or the Linux command line. Among those, he shares a love of tabletop RPG games, reading fantasy novels, and spending time with his wife and two daughters. Disclaimer: The examples presented in this post are hypothetical ideas of how to achieve similar types of results. They are not the utmost best solution(s). The majority, if not all, of the examples provided, is performed on a personal development/learning workstation-environment and should not be considered production quality or ready. Your particular goals and needs may vary. Use those practices that best benefit your needs and goals. Opinions are my own. The post Basic Data Analysis with MySQL Shell Python mode appeared first on Digital Owl's Prose. https://joshuaotwell.com/basic-data-analysis-with-mysql-shell-python-mode/
0 notes
Text
Running a Lasso Regression Analysis
Hey guy’s so far we have seen how to run classification trees and random forest analysis. So now let's see how we test a Lasso regression model in Python.
First, I will call in the libraries that I will need. In addition to the pandas, numpy, and matplotlib libraries I'll need the train_test_split function from the sklearn.cross_validation library, and the LassoLarsCV function from the sklearn.linear_model library.
After I call in the data set using the pd.read_csv function, I'll do a little extra data management. Namely, I want to create a new dataset called data_clean in which I will delete observations with missing data on any of the variables using the dropna function.
Then, I want to create a variable for gender called male, that is coded zero for female and one for male, like the other binary variables in the data set.
#from pandas import Series, DataFrame import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pylab as plt from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LassoLarsCV
#Load the dataset data = pd.read_csv("tree_addhealth.csv")
#upper-case all DataFrame column names data.columns = map(str.upper, data.columns)
# Data Management data_clean = data.dropna() recode1 = {1:1, 2:0} data_clean['MALE']= data_clean['BIO_SEX'].map(recode1)
Next, I will create two data frames. The first, called predvar, P-R-E-D-V-A-R, will include only the predictor variables that I will use in the lasso regression model. The second, called target, will include only my school connectedness response variable.
#select predictor variables and target variable as separate data sets predvar= data_clean[['MALE','HISPANIC','WHITE','BLACK','NAMERICAN','ASIAN', 'AGE','ALCEVR1','ALCPROBS1','MAREVER1','COCEVER1','INHEVER1','CIGAVAIL','DEP1', 'ESTEEM1','VIOL1','PASSIST','DEVIANT1','GPA1','EXPEL1','FAMCONCT','PARACTV', 'PARPRES']]
target = data_clean.SCHCONN1
In lasso regression, the penalty term is not fair if the predictive variables are not on the same scale, meaning that not all the predictors get the same penalty. So I will standardize all the predictors to have a mean equal to zero and a standard deviation equal to one, including my binary predictors, which will put them all on the same scale.
To standardize the predictors, I'm going to first create a copy of my predvar data frame and name it predictors. Then, I'm going to import the preprocessing function from the sklearn library.
# standardize predictors to have mean=0 and sd=1 predictors=predvar.copy()
I will list the name of my predictor variable = preprocessing.scale. The preprocessing.scale function transforms the variable to have a mean of zero and a standard deviation of one, thus putting all the predictors on the same scale. Then, in parentheses I type the name of my variable again, and add .astype('float64'). The as type float 64 code ensures that my predictors will have a numeric format.
from sklearn import preprocessing predictors['MALE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['MALE'].astype('float64')) predictors['HISPANIC']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['HISPANIC'].astype('float64')) predictors['WHITE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['WHITE'].astype('float64')) predictors['NAMERICAN']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['NAMERICAN'].astype('float64')) predictors['ASIAN']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ASIAN'].astype('float64')) predictors['AGE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['AGE'].astype('float64')) predictors['ALCEVR1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ALCEVR1'].astype('float64')) predictors['ALCPROBS1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ALCPROBS1'].astype('float64')) predictors['MAREVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['MAREVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['COCEVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['COCEVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['INHEVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['INHEVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['CIGAVAIL']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['CIGAVAIL'].astype('float64')) predictors['DEP1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['DEP1'].astype('float64')) predictors['ESTEEM1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ESTEEM1'].astype('float64')) predictors['VIOL1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['VIOL1'].astype('float64')) predictors['PASSIST']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PASSIST'].astype('float64')) predictors['DEVIANT1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['DEVIANT1'].astype('float64')) predictors['GPA1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['GPA1'].astype('float64')) predictors['EXPEL1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['EXPEL1'].astype('float64')) predictors['FAMCONCT']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['FAMCONCT'].astype('float64')) predictors['PARACTV']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PARACTV'].astype('float64')) predictors['PARPRES']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PARPRES'].astype('float64'))
In the next line of code, I will use the train test split function from the sklearn cross validation library to randomly split my data set into a training data set consisting of 70% of the total observations in the data set. And a test data set consisting of the other 30% of the observations. First, I list the two training data sets.
The first data set, called pred_train, will include the predictor variables from my training data set and a second data set, called pred_test, will include the predictor variables from my test data set. The third data set, called tar_train, will include the response variable from my training data set and the fourth data set, called tar_test, will include the response variable for my test data set.
Then I type the function name, train_test_split and in parentheses, I list my full predictors and target data set names with commas separating them. The test_size option tells Python to randomly place 30% of the observations in the pred_test and pred_tar test data sets. By default, the other 70% of the observations are placed in the pred_train and tar_train training data sets.
The random_state option specifies a random number seed to ensure that the data are randomly split the same way if I run the code again.
# split data into train and test sets pred_train, pred_test, tar_train, tar_test = train_test_split(predictors, target, test_size=.3, random_state=123)
Complete Code
#from pandas import Series, DataFrame import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pylab as plt from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split from sklearn.linear_model import LassoLarsCV
#Load the dataset data = pd.read_csv("tree_addhealth.csv")
#upper-case all DataFrame column names data.columns = map(str.upper, data.columns)
# Data Management data_clean = data.dropna() recode1 = {1:1, 2:0} data_clean['MALE']= data_clean['BIO_SEX'].map(recode1)
#select predictor variables and target variable as separate data sets predvar= data_clean[['MALE','HISPANIC','WHITE','BLACK','NAMERICAN','ASIAN', 'AGE','ALCEVR1','ALCPROBS1','MAREVER1','COCEVER1','INHEVER1','CIGAVAIL','DEP1', 'ESTEEM1','VIOL1','PASSIST','DEVIANT1','GPA1','EXPEL1','FAMCONCT','PARACTV', 'PARPRES']]
target = data_clean.SCHCONN1
# standardize predictors to have mean=0 and sd=1 predictors=predvar.copy() from sklearn import preprocessing predictors['MALE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['MALE'].astype('float64')) predictors['HISPANIC']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['HISPANIC'].astype('float64')) predictors['WHITE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['WHITE'].astype('float64')) predictors['NAMERICAN']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['NAMERICAN'].astype('float64')) predictors['ASIAN']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ASIAN'].astype('float64')) predictors['AGE']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['AGE'].astype('float64')) predictors['ALCEVR1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ALCEVR1'].astype('float64')) predictors['ALCPROBS1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ALCPROBS1'].astype('float64')) predictors['MAREVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['MAREVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['COCEVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['COCEVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['INHEVER1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['INHEVER1'].astype('float64')) predictors['CIGAVAIL']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['CIGAVAIL'].astype('float64')) predictors['DEP1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['DEP1'].astype('float64')) predictors['ESTEEM1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['ESTEEM1'].astype('float64')) predictors['VIOL1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['VIOL1'].astype('float64')) predictors['PASSIST']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PASSIST'].astype('float64')) predictors['DEVIANT1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['DEVIANT1'].astype('float64')) predictors['GPA1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['GPA1'].astype('float64')) predictors['EXPEL1']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['EXPEL1'].astype('float64')) predictors['FAMCONCT']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['FAMCONCT'].astype('float64')) predictors['PARACTV']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PARACTV'].astype('float64')) predictors['PARPRES']=preprocessing.scale(predictors['PARPRES'].astype('float64'))
# split data into train and test sets pred_train, pred_test, tar_train, tar_test = train_test_split(predictors, target, test_size=.3, random_state=123)
# specify the lasso regression model model=LassoLarsCV(cv=10, precompute=False).fit(pred_train,tar_train)
# print variable names and regression coefficients dict(zip(predictors.columns, model.coef_))
# plot coefficient progression m_log_alphas = -np.log10(model.alphas_) ax = plt.gca() plt.plot(m_log_alphas, model.coef_path_.T) plt.axvline(-np.log10(model.alpha_), linestyle='--', color='k', label='alpha CV') plt.ylabel('Regression Coefficients') plt.xlabel('-log(alpha)') plt.title('Regression Coefficients Progression for Lasso Paths')
# plot mean square error for each fold m_log_alphascv = -np.log10(model.cv_alphas_) plt.figure() plt.plot(m_log_alphascv, model.cv_mse_path_, ':') plt.plot(m_log_alphascv, model.cv_mse_path_.mean(axis=-1), 'k', label='Average across the folds', linewidth=2) plt.axvline(-np.log10(model.alpha_), linestyle='--', color='k', label='alpha CV') plt.legend() plt.xlabel('-log(alpha)') plt.ylabel('Mean squared error') plt.title('Mean squared error on each fold')
# MSE from training and test data from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error train_error = mean_squared_error(tar_train, model.predict(pred_train)) test_error = mean_squared_error(tar_test, model.predict(pred_test)) print ('training data MSE') print(train_error) print ('test data MSE') print(test_error)
# R-square from training and test data rsquared_train=model.score(pred_train,tar_train) rsquared_test=model.score(pred_test,tar_test) print ('training data R-square') print(rsquared_train) print ('test data R-square') print(rsquared_test)
0 notes
Link
A data frame is a method for storing data in rectangular grids for easy overview. If you have knowledge of java development and R basics, then you must be aware of the data frames. The measurements or values of an instant corresponds to the rows in the grid whereas the vectors containing data for a specific variable represent the column.
0 notes
Text
Week 3:
I put here the script, the results and its description:
PYTHON:
Created on Thu May 22 14:21:21 2025
@author: Pablo """
libraries/packages
import pandas import numpy
read the csv table with pandas:
data = pandas.read_csv('C:/Users/zop2si/Documents/Statistic_tests/nesarc_pds.csv', low_memory=False)
show the dimensions of the data frame:
print() print ("length of the dataframe (number of rows): ", len(data)) #number of observations (rows) print ("Number of columns of the dataframe: ", len(data.columns)) # number of variables (columns)
variables:
variable related to the background of the interviewed people (SES: socioeconomic status):
biological/adopted parents got divorced or stop living together before respondant was 18
data['S1Q2D'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S1Q2D'], errors='coerce')
variable related to alcohol consumption
HOW OFTEN DRANK ENOUGH TO FEEL INTOXICATED IN LAST 12 MONTHS
data['S2AQ10'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S2AQ10'], errors='coerce')
variable related to the major depression (low mood I)
EVER HAD 2-WEEK PERIOD WHEN FELT SAD, BLUE, DEPRESSED, OR DOWN MOST OF TIME
data['S4AQ1'] = pandas.to_numeric(data['S4AQ1'], errors='coerce')
Choice of thee variables to display its frequency tables:
string_01 = """ Biological/adopted parents got divorced or stop living together before respondant was 18: 1: yes 2: no 9: unknown -> deleted from the analysis blank: unknown """
string_02 = """ HOW OFTEN DRANK ENOUGH TO FEEL INTOXICATED IN LAST 12 MONTHS
Every day
Nearly every day
3 to 4 times a week
2 times a week
Once a week
2 to 3 times a month
Once a month
7 to 11 times in the last year
3 to 6 times in the last year
1 or 2 times in the last year
Never in the last year
Unknown -> deleted from the analysis BL. NA, former drinker or lifetime abstainer """
string_02b = """ HOW MANY DAYS DRANK ENOUGH TO FEEL INTOXICATED IN THE LAST 12 MONTHS:
"""
string_03 = """ EVER HAD 2-WEEK PERIOD WHEN FELT SAD, BLUE, DEPRESSED, OR DOWN MOST OF TIME:
Yes
No
Unknown -> deleted from the analysis """
replace unknown values for NaN and remove blanks
data['S1Q2D']=data['S1Q2D'].replace(9, numpy.nan) data['S2AQ10']=data['S2AQ10'].replace(99, numpy.nan) data['S4AQ1']=data['S4AQ1'].replace(9, numpy.nan)
create a subset to know how it works
sub1 = data[['S1Q2D','S2AQ10','S4AQ1']]
create a recode for yearly intoxications:
recode1 = {1:365, 2:313, 3:208, 4:104, 5:52, 6:36, 7:12, 8:11, 9:6, 10:2, 11:0} sub1['Yearly_intoxications'] = sub1['S2AQ10'].map(recode1)
create the tables:
print() c1 = data['S1Q2D'].value_counts(sort=True) # absolute counts
print (c1)
print(string_01) p1 = data['S1Q2D'].value_counts(sort=False, normalize=True) # percentage counts print (p1)
c2 = sub1['Yearly_intoxications'].value_counts(sort=False) # absolute counts
print (c2)
print(string_02b) p2 = sub1['Yearly_intoxications'].value_counts(sort=True, normalize=True) # percentage counts print (p2) print()
c3 = data['S4AQ1'].value_counts(sort=False) # absolute counts
print (c3)
print(string_03) p3 = data['S4AQ1'].value_counts(sort=True, normalize=True) # percentage counts print (p3)
RESULTS:
Biological/adopted parents got divorced or stop living together before respondant was 18: 1: yes 2: no 9: unknown -> deleted from the analysis blank: unknown
2.0 0.814015 1.0 0.185985 Name: S1Q2D, dtype: float64
HOW MANY DAYS DRANK ENOUGH TO FEEL INTOXICATED IN THE LAST 12 MONTHS:
0.0 0.651911 2.0 0.162118 6.0 0.063187 12.0 0.033725 11.0 0.022471 36.0 0.020153 52.0 0.019068 104.0 0.010170 208.0 0.006880 365.0 0.006244 313.0 0.004075 Name: Yearly_intoxications, dtype: float64
EVER HAD 2-WEEK PERIOD WHEN FELT SAD, BLUE, DEPRESSED, OR DOWN MOST OF TIME:
Yes
No
Unknown -> deleted from the analysis
2.0 0.697045 1.0 0.302955 Name: S4AQ1, dtype: float64
Description:
In regard to computing: the unknown answers were substituted by nan and therefore not considered for the analysis. The original responses to the number of yearly intoxications, which were not a direct figure, were transformed by mapping to yield the actual number of yearly intoxications. For doing this, a submodel was also created.
In regard to the content:
The first variable is quite simple: 18,6% of the respondents saw their parents divorcing before they were 18 years old.
The second variable is the number of yearly intoxications. The highest frequency is as expected not a single intoxication in the last 12 months (65,19%). The more the number of intoxications, the smaller the probability, with an only exception: 0,6% got intoxicated every day and 0,4% got intoxicated almost everyday. I would have expected this numbers flipped.
The last variable points a relatively high frequency of people going through periods of sadness: 30,29%. However, it isn´t yet enough to classify all these periods of sadness as low mood or major depression. A further analysis is necessary.
0 notes
Link
A data frame is a method for storing data in rectangular grids for easy overview. If you have knowledge of java development and R basics, then you must be aware of the data frames. The measurements or values of an instant corresponds to the rows in the grid whereas the vectors containing data for a specific variable represent the column. Hence, the rows in the data frame can include values like numeric, character, logical and so on.
0 notes
Text
ANOVA & post hoc
In this task, I’ll try to find out if connection exists between average daily ethanol consumption (in ounces) of a person and their mood (how often they felt depressive/downhearted during 4 weeks prior to the survey).
Here is some information about those variables.
Explanatory variable: categorical, 5 categories (unknown values will be deleted since they do not give any useful information).
S1Q213 DURING PAST 4 WEEKS, HOW OFTEN FELT DOWNHEARTED AND DEPRESSED
1. All of the time
2. Most of the time
3. Some of the time
4. A little of the time
5. None of the time
9. Unknown
Response variable, quantitative (blanks to be deleted later).
ETOTLCA2 AVERAGE DAILY VOLUME OF ETHANOL CONSUMED IN PAST YEAR, FROM ALL
TYPES OF ALCOHOLIC BEVERAGES COMBINED
0.0003 - 219.9555 Ounces of ethanol
Blank Unknown
Let’s formulate our null hypothesis first: there is no relation between presence of depression ( and severity of it) and their drinking habits ( = all means are equal).
An alternative hypothesis would be that there is some kind of a relation between daily ethanol consumption and depression.
To test the hypothesis, I conducted an Analysis of Variance with Python.
In order to do that, I did the following:
1) Importing necessary libraries
import numpy
import pandas
import statsmodels.formula.api as smf
2) Read the csv file of the dataset and fix the numeric datatypes
data = pandas.read_csv("nesarc.csv", low_memory=False)
data = data.apply(pandas.to_numeric, errors='coerce')
3) After examining the data, I found out that the explanatory variable (S1Q213, DURING PAST 4 WEEKS, HOW OFTEN FELT DOWNHEARTED AND DEPRESSED) had some missing values (replaced by ‘9’s). These do not bear any meaning and thus useless for the analysis, so I replaced them with NaNs to delete them later.
data['S1Q213'].replace(9, numpy.nan, inplace=True)
4) Deleting rows with NaNs present in columns related to variables that I’ll use.
data2 = data[['ETOTLCA2','S1Q213']].dropna()
5) Creating an ordinary least squares regression model to find out the needed F-statistic and p-value, fitting and printing the summary of the model.
model2 = smf.ols(formula = "ETOTLCA2 ~ C(S1Q213)", data = data2)
results2=model2.fit()
print(results2.summary())
OLS Regression Results
==============================================================================
Dep. Variable: ETOTLCA2 R-squared: 0.003
Model: OLS Adj. R-squared: 0.003
Method: Least Squares F-statistic: 20.23
Date: Sun, 21 Oct 2018 Prob (F-statistic): 1.18e-16
Time: 02:11:35 Log-Likelihood: -58890.
No. Observations: 26598 AIC: 1.178e+05
Df Residuals: 26593 BIC: 1.178e+05
Df Model: 4
Covariance Type: nonrobust
Here’s what we need: F=20.23 and p=1.18e-16. Now, we can see that p-value is much less than 0.05, which means we reject our null hypothesis that there is no relation between severity of a person’s depression (or lack of it) and amount of ethanol consumed daily. It appears that there is some kind of association between those two variables. To find out which categories are associated, I’ll do some post hoc comparisons.
1) Importing necessary tools:
import statsmodels.stats.multicomp as multi
2) Doing a Tukey's HSD (Honestly Significant Difference) test
mc = multi.MultiComparison(data2['ETOTLCA2'],data2['S1Q213'])
res = mc.tukeyhsd()
print(res.summary())
Multiple Comparison of Means - Tukey HSD,FWER=0.05
=============================================
group1 group2 meandiff lower upper reject
---------------------------------------------
1.0 2.0 0.0092 -0.3321 0.3506 False
1.0 3.0 -0.3533 -0.6595 -0.0471 True
1.0 4.0 -0.4278 -0.7254 -0.1301 True
1.0 5.0 -0.5062 -0.8006 -0.2119 True
2.0 3.0 -0.3625 -0.5685 -0.1565 True
2.0 4.0 -0.437 -0.6301 -0.2439 True
2.0 5.0 -0.5155 -0.7033 -0.3276 True
3.0 4.0 -0.0745 -0.195 0.046 False
3.0 5.0 -0.153 -0.2649 -0.041 True
4.0 5.0 -0.0785 -0.1644 0.0074 False
---------------------------------------------
Which means that the significant differences are present between the categories 1 and 3, 4, 5; 2 and 3, 4, 5; 3 and 5.
What categories mean:
All of the time
Most of the time
Some of the time
A little of the time
None of the time
It appears that there is no significant difference between alcohol consumption of people who are depressed constantly and most of the time. Moreover, those who were sad a little of the time and not depressed at all are also likely to drink about the same amount.
On the other hand, all the other categories’ means were proven to be significantly different. Which means, for example, that drinking habits of a person that was depressed all the time are statistically different from habits of people who were sad for some time or less. To find out how much are they different exactly, let’s compare their means.
m1 = data2.groupby('S1Q213').mean()
print(m1)
sd1 = data2.groupby('S1Q213').std()
print(sd1)
�� ETOTLCA2
S1Q213
1.0 0.998476
2.0 1.007703
3.0 0.645213
4.0 0.570721
5.0 0.492227
ETOTLCA2
S1Q213
1.0 2.595513
2.0 4.989636
3.0 1.683092
4.0 2.868919
5.0 1.359950
As we can see, the more often they felt depressive during 4 weeks prior to the survey, the more they are likely to drink daily on average.
Summary:
ANOVA revealed that among people who consume ethanol, severity of their depression (or lack of it) (split into 5 ordered categories, which is the categorical explanatory variable) and amount of ethanol consumed daily on average (quantitative response variable) were significantly associated, F=20.23, p<0.0001.
Post hoc comparisons of mean amount of ethanol consumed with pairs of depression severity categories revealed that people who are more depressed are more likely to drink more. However, there was no significant difference in drinking levels of people depressed most and all of the time. The same is true for the two least depressed categories. So we could’ve probably reduced number of categories to three: very depressed, moderately depressed and slightly or not depressed, because we found out that significant differences were only found between these greater categories (very depressed people drink more than moderately depressed, who in turn drink more than slightly or not depressed at all), while no statistically important differences in means were found within those categories (depressed all the time and most of the time drink the same amount, the same is true for depressed for a little and not depressed at all).
0 notes
Text
350+ TOP PYTHON Interview Questions and Answers
PYTHON Interview Questions for freshers & experienced :-
1) What Is Python? Python is an interpreted, interactive, object-oriented programming language. It incorporates modules, exceptions, dynamic typing, very high level dynamic data types, and classes. Python combines remarkable power with very clear syntax. It has interfaces to many system calls and libraries, as well as to various window systems, and is extensible in C or C++. It is also usable as an extension language for applications that need a programmable interface. Finally, Python is portable: it runs on many Unix variants, on the Mac, and on PCs under MS-DOS, Windows, Windows NT, and OS/2. 2) What are the different ways to create an empty NumPy array in python? There are two methods we can apply to create empty NumPy arrays. The first method. import numpy numpy.array() The second method. # Make an empty NumPy array numpy.empty(shape=(0,0)) 3) Can’t concat bytes to str? This is providing to be a rough transition to python on here f = open( ‘myfile’, ‘a+’ ) f.write(‘test string’ + ‘\n’) key = “pass:hello” plaintext = subprocess.check_output() print (plaintext) f.write (plaintext + ‘\n’) f.close() The output file looks like: test string 4) Expline different way to trigger/ raise exception in your python script? Raise used to manually raise an exception general-form: raise exception-name (“message to be conveyed”). voting_age = 15 if voting_age output: ValueError: voting age should be at least 19 and above 2.assert statements are used to tell your program to test that condition attached to assert keyword, and trigger an exception whenever the condition becomes false. Eg: a = -10 assert a > 0 #to raise an exception whenever a is a negative number Output: AssertionError Another way of raising an exception can be done by making a programming mistake, but that is not usually a good way of triggering an exception 5) Why is not__getattr__invoked when attr==’__str__’? The base class object already implements a default __str__ method, and __getattr__function is called for missing attributes. The example as it we must use the __getattribute__ method instead, but beware of the dangers. class GetAttr(object): def __getattribute__(self, attr): print(‘getattr: ‘ + attr) if attr == ‘__str__’: return lambda: ‘’ else: return lambda *args: None A better and more readable solution to simply override the __str__ method explicitly. class GetAttr(object): def __getattr__(self, attr): print(‘getattr: ‘ + attr) return lambda *args: None def __str__(self): return ‘’ 6)What do you mean by list comprehension? The process of creating a list performing some operation on the data so that can be accessed using an iterator is referred to as list comprehension. EX: Output: 65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90 7) What will be the output of the code:def foo (i=)? i.append (1) return i >>> foo () >>> foo () Output: The argument to the function foo is evaluated once when the function is defined However since it is a list on every all the list is modified by appending a 1 to it. 8) How to Tic tac toe computer move? Below The code of computer move in the game tic tac toe in python def computermove(board,computer,human): movecom=” rmoves=rd(0,8) for movecom in legalmoves(board): board=computer if winner(board)==computer: return movecom board=” for movecom in legalmoves(board): board=human if winner(board)==human: return movecom board=” while rmoves not in legalmoves(board): rtmoves=rd(0,8) return rmoves 9) Explain about ODBC and python? ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) API standard allows the connections with any database that supports the interface such as the PostgreSL database or Microsoft access in a transparent manner Three types of ODBC modules for python: PythonWin ODBC module – limited development mxODBC – a commercial product pyodbc – This is open source python package 10) How to implement the decorator function, using dollar ()? Code: def dollar(fn): def new(*args): return ‘$’ + str(fn(*args)) return new @dollar def price(amount, tax_rate): return amount + amount*tax_rate print price(100,0.1) output: $110

PYTHON Interview Questions 11) How to count the number of instance? You have a class A, you want to count the number of A instance. Hint: use staticmethod Example class A: total = 0 def __init__(self, name): self.name = name A.total += 1 def status(): print “Number of instance (A) : “, A.total status = staticmethod(status) a1 = A(“A1”) a2 = A(“A2”) a3 = A(“A3”) a4 = A(“A4”) A.status() Output: The number of instance (A) : 4 12) What are the Arithmetic Operators that Python supports? ‘+’ : Addition ‘-’ : Subtraction ‘*’ : Multiplication ‘/’: Division ‘%’: Modulo division ‘**’: Power Of ‘//’: floor div Python does not support unary operators like ++ or – operators. Python supports “Augmented Assignment Operators”. i.e., A += 10 Means A = A+10 B -= 10 Means B = B-10 13) How do you reload a Python module? All that needs to be a module object to the imp.reload() function or just reload() in Python 2.x, and the module will be reloaded from its source file. Any other code references symbols exported by the reloaded module, they still are bound to the original code. 14) How does Python handle Compile-time and Run-time code checking? Python supports compile-time code checking up to some extent. Most checks for variable data types will be postponed until run-time code checking. When an undefined custom function is used, it will move forward with compile-time checking. During runtime, Python raises exceptions against errors. 15) What are Supporting Python packages for data science operations? Pandas: A package providing flexible data structures to work with relational or labeled data. NumPy: A package that allows working with numerical based data structures like arrays and tensors. Matplotlib: A 2D rendering engine written for Python. Tensorflow: A package used for constructing computational graphs. 16) What are the ones that can be used with pandas? A python dict, ndarray or scalar values can be used with Pandas. The passed index is a list of axis labels. 17) How To Add an Index, Row or Column to a Pandas DataFrame? The index can be added by calling set_index() on programmer DataFrame. For accessing rows, loc works on labels of programme index, iloc works on the positions in programme index, it is a more complex case: when the index is integer-based, programmer passes a label to ix. 18) How To Create an Empty DataFrame? The function that programmer will use is the Pandas Dataframe() function: it reuires the programmer to pass the data that programmer wants to put in, the indices and the columns. 19) Does Pandas Recognize Dates When Importing Data? Yes. but programmer needs to help it a tiny bit: add the argument parse_dates when programmer by reading in data from, let is say, a comma-separated value (CSV) file. 20) How to convert a NumPy array to a Python List? Use tolist(): import numpy as np >>> np.array(,]).tolist() , ] 21) How to set the figure title and axes labels font size in Matplotlib? Functions dealing with text like label, title, etc. accept parameters same as matplotlib.text.Text. For the font size you can use size/fontsize: 39) What is dictionary in Python? The built-in datatypes in Python are called a dictionary. It defines one-to-one Relationship between keys and values. It contains a pair of keys and their corresponding values. Dictionaries are indexed by keys. It is a collection which is unordered, changeable and indexed. Let’s take an example: The following example contains some keys. State, Capital,Language. Their corresponding values are Karnataka, Bangalore, and Kannada respectively. Dict={ ‘Country’:’Karnataka’,’Capital’:’Bangalore’,’Launguage’:’Kannada’} print dict Karnataka Print dict Bangalore Print dict Kannada 40) How memory is managed in Python? Python private heap space manages python memory. Python heap has all Python objects and data structures. Access to this private heap is restricted to programmer also Python private heap is taken care by the interpreter. The core API gives access to some tools for the programmer to code. Python memory manager allocates python heap space. 41)What is the output of this following statement? f=none for i in range(5); with open(“data.txt”, ”w”) as f: if I>1: break print f.closed A) True B) False C) None D) Error Ans: A 42) Write a coding in Find a Largest Among three numbers? num1 = 10 num2 = 14 num3 = 12 if (num1 >= num2) and (num1 >= num3): largest = num1 elif (num2 >= num1) and (num2 >= num3): largest = num2 else: largest = num3 print(“The largest number between”,num1,”,”,num2,”and”,num3,”is”,largest) Output: The largest Number is 14.0 43) What is Lambda in Python? lambda is an one line anonymous function, Example: Sum=lambda i,c:i+c 44) What is the difference between list and tuples? Lists are the mutable elements where we can able to perform the task in the existed variable. Lists can able to reduce the utilization of memory Tuples are immutable so it can execute faster when compared with list. But it will wastes the memory. 45) What are the key features of Python? The python doesn’t have any header files It doesn’t have any structure or syntax except the indentation. It can execute the instructions fastly because of the RISC architecture. It consumes only less memory because of no internal executions. It doesn’t have any compilers compilation can be done at the time of the program. 46) How to delete a file in Python? In Python, Delete a file using this command, os.unlink(filename) or os.remove (filename) 47) What is the usage of help() and dir() function in Python? Help() and dir() both functions are accessible from the Python interpreter used for viewing a consolidated dump of built-in functions. Help() function: The help() function is used to display the documentation string and also facilitates you to see the help related to modules, keywords, attributes, etc. 48) Which of the following statements create a dictionary? (Multiple Correct Answers Possible) a) d = {} b) d = {“john”:40, “peter”:45} c) d = {40:”john”, 45:”peter”} d) d = (40:”john”, 45:”50”) Ans: All of the above 49) Which of the following is an invalid statement? a) abc = 1,000,000 b) a b c = 1000 2000 3000 c) a,b,c = 1000, 2000, 3000 d) a_b_c = 1,000,000 Ans: c 50) What is the output of the following? try: if ‘1’ != 1: raise “someError” else: print(“someError has not occured”) except “someError”: print (“someError has occured”) a) someError has occured b) someError has not occured c) invalid code d) none of the above Ans: b 51) What is the maximum possible length of an identifier? a) 31 characters b) 63 characters c) 79 characters d) None of the above Ans: d 52) Differentiate list and tuple with an example? difference is that a list is mutable, but a tuple is immutable. Example: >>> mylist= >>> mylist=2 >>> mytuple=(1,3,3) >>> mytuple=2 TypeError: ‘tuple’ object does not support item assignment 53) Which operator will be helpful for decision making statements? comparison operator 54) Out of two options which is the template by default flask is following? a) Werkzeug b) Jinja2 Ans : b 55) Point out the use of help() function Help on function copy in module copy: copy(x) Shallow copy operation on arbitrary Python objects. 56) From below select which data structure is having key-value pair ? a.List b.Tuples c.Dictionary Ans : c 57) Differentiate *args and **kwargs? *args : We can pass multiple arguments we want like list or tuples of data **kwargs : we can pass multiple arguments using keywords 58) Use of Negative indices? It helps to slice from the back mylist= >>>mylist 6 59) Give an example for join() and split() funcitons >>> ‘,’.join(‘12345’) ‘1,2,3,4,5’ >>> ‘1,2,3,4,5’.split(‘,’) 60) Python is case sensitive ? a.True b.False Ans : a 61) List out loop breaking functions break continue pass 62) what is the syntax for exponentiation and give example? a**b 2**3 = 8 63) Which operator helps to do addition operations ? arithmetic operator 64) How to get all keys from dictionary ? dictionary_var.keys() 65) Give one example for multiple statements in single statement? a=b=c=3 66) What is the output for the following code? >> def expandlist(val, list=): list.append(val) return list >>> list1 = expandlist (10) >>> list2 = expandlist (123,) >>> list3 = expandlist (‘a’) >>> list1,list2,list3 Ans : (, , ) 67) Number of argument’s that range() function can take ? 3 68) Give an example to capital first letter of a string? a=’test’ print a.upper() Test 69) How to find whether string is alphanumeric or not? str = “hjsh#”; print str.isalnum() Ans :False 70) Which method will be used to delete a file ? os.remove(filename) 71) What is difference between match & search in regex module in python? Match Checks for a match only at the beginning of the string, while search checks for a match anywhere in the string. 72) Can we change tuple values? If yes, give an example. Since tuple are immutable, so we cannot change tuple value in its original form but we can convert it into list for changing its values and then convert again to tuple. Below is the example: my_tuple=(1,2,3,4) my_list=list(my_tuple) my_list=9 my_tuple=tuple(my_list) 73) What is purpose of __init__ in Class ? Is it necessary to use __init__ while creating a class ? __init__ is a class contructor in python. __init__ is called when we create an object for a class and it is used to initialize the attribute of that class. eg : def __init__ (self, name ,branch , year) self.name= name self.branch = branch self.year =year print(“a new student”) No, It is not necessary to include __init__ as your first function every time in class. 74) Can Dictionary have a duplicate keys ? Python Doesn’t allow duplicate key however if a key is duplicated the second key-value pair will overwrite the first as a dictionary can only have one value per key. For eg : >>> my_dict={‘a’:1 ,’b’ :2 ,’b’:3} >>> print(my_dict) {‘a’: 1, ‘b’: 3} 75) What happened if we call a key that is not present in dictionary and how to tackle that kind of error ? It will return a Key Error . We can use get method to avoid such condition. This method returns the value for the given key, if it is present in the dictionary and if it is not present it will return None (if get() is used with only one argument). Dict.get(key, default=None) 76) What is difference b/w range and arange function in python? numpy.arange : Return evenly spaced values within a given interval. Values are generated within the half-open interval stop, dtype=None) Range : The range function returns a list of numbers between the two arguments (or one) you pass it. 77) What is difference b/w panda series and dictionary in python? Dictionaries are python’s default data structures which allow you to store key: value pairs and it offers some built-in methods to manipulate your data. 78) Why it need to be create a virtual environment before staring an project in Django ? A Virtual Environment is an isolated working copy of Python which allows you to work on a specific project without worry of affecting other projects. Benefit of creating virtualenv : We can create multiple virtualenv , so that every project have a different set of packages . For eg. if one project we run on two different version of Django , virtualenv can keep thos projects fully separate to satisfy both reuirements at once.It makes easy for us to release our project with its own dependent modules. 79) How to write a text from from another text file in python ? Below is the code for the same. import os os.getcwd() os.chdir(‘/Users/username/Documents’) file = open(‘input.txt’ ,’w’) with open(“output.txt”, “w”) as fw, open(“input.txt”,”r”) as fr: 80) what is difference between input and raw_input? There is no raw_input() in python 3.x only input() exists. Actually, the old raw_input() has been renamed to input(), and the old input() is gone, but can easily be simulated by using eval(input()). In python 3.x We can manually compile and then eval for getting old functionality. python2.x python3.x raw_input() input() input() eval(input()) 81) What are all important modules in python reuired for a Data Science ? Below are important module for a Data Science : NumPy SciPy Pandas Matplotlib Seaborn Bokeh Plotly SciKit-Learn Theano TensorFlow Keras 82) What is use of list comprehension ? List comprehensions is used to transform one list into another list. During this process, list items are conditionally included in the new list and each items are transformed as reuired. Eg. my_list= my_list1= Using “for “ loop : for i in my_list1: my_list.append(i*2) Using List comprehension : my_list2= print(my_list2) 83) What is lambda function ? lambda function is used for creating small, one-time and anonymous function objects in Python. 84) what is use of set in python? A set is a type of python data Structure which is unordered and unindexed. It is declared in curly braces . sets are used when you reuired only uniue elements .my_set={ a ,b ,c,d} 85) Does python has private keyword in python ? how to make any variable private in python ? It does not have private keyword in python and for any instance variable to make it private you can __ prefix in the variable so that it will not be visible to the code outside of the class . Eg . Class A: def __init__(self): self.__num=345 def printNum(self): print self.__num 86) What is pip and when it is used ? it is a package management system and it is used to install many python package. Eg. Django , mysl.connector Syntax : pip install packagename pip install Django : to install Django module 87) What is head and tail method for Data frames in pandas ? Head : it will give the first N rows of Dataframe. Tail : it will give last N rows of Dataframe. By default it is 5. 88) How to change a string in list ? we can use split method to change an existing string into list. s= ‘Hello sam good morning ’ s.split() print(s) 89) How to take hello as output from below nested list using indexing concepting in python. my_list=, 4,5]],3,4] Ans : my_list print(my_list) 90) What is list when we have to use ? Lists always store homogeneous elements. we have to use the lists when the data is same type and when accessing is more insteading of inserting in memory. 91) What is dict when we have to use ? Dict is used to store key value pairs and key is calculated using hash key. This is used when we want to access data in O(1) time as big O notation in average case. Dict I used in u can say super market to know the price of corresponding while doing billing 92) What is tuple when we have to use ? Tuple is hetrogenous and we have to use when data is different types. 93) Is String Immutable ? Yes because it creates object in memory so if you want to change through indexing it will throw an exception since it can’t be changes I,e immutable. 94) How to handle Exception ? We can handle exceptions by using try catch block . we can also else block in python to make it executed based on condition. 95) Will python work multiple inheritance? Yes it works .by seuentially referring parent class one by one. 96) Will class members accessible by instances of class? Yes by referring corresponding attributes we can access. 97) What are Special methods in python and how to implement? Special methods in python are __init__,__str__,__iter__,__del__ __init__-it will initialize when class loads. __str__-It is used to represent object in a string format. __iter__-it I used to define iteration based on reuirements. __del__-It is used to destroy object when it is not reuired for memory optimization. 98) How to handle deadlock in python. By providing synchronization methods so that each thread access one at a time.It will lock another thread until thread fine it execution. 99) How for loop will works in python? For loop internally calls iter method of an object for each call. 100) What is List comprehension how to define it and when to use? List Comprehensions are expression based iteration. So we have to give expression and then provide loop and provide if condition if needed. We have to use when we want to define in such a way that write the code in a compact way. 101) What is set when we have to use? Set is used to define uniue elements without duplicates. So if you have lump of data and we are searching through email record. By using set we can get the uniue elements. 102) How django works ? Django will take an url from frontend and look for url reolvers and url will ap corresponding view and if data to be handled it will use certain model to make any database transactions and give repone via view and then passs to UI. Or django template 103) Is python pure object oriented programming ? Yes in python all types are stored a objects. 104) What are packages in python which are commonly used explain one ? The packages used are os, sys,time,tempfile,pdb, Os –it is used for file and directories handling. Pdb-It is used to debug the code to find the root cause of issue. 105) How will you merge 2 dictionaries in python? a = {1:’1’} , b={2:’2’} c= {**a,**b} 106) What is the other way of checking truthiness? These only test for truthiness: if x or y or z: print(‘passed’) if any((x, y, z)): print(‘passed’) 107) How will you verify different flags at once? flags at once in Python v1,v2,v3 = 0, 1, 0 if v1 == 1 or v2 == 1 or v3 == 1: print(‘passed’) if 1 in (v1, v2, v3): print(‘passed’) 108) What happens when you execute python == PYTHON? You get a Name Error Execution 109) Tool used to check python code standards? Pylint 110) How strings can be sliced? They can be generally treated as arrays without commas. Eg: a = “python” a -> i can be any number within the length of the string 111) How to pass indefinite number of arguments to any function? We use **args when we don’t know the number of arguments to be passed 112) In OOPS what is a diamond problem in inheritance? During multiple inheritance, when class X has two subclasses Y and Z, and a class D has two super classes Y and Z.If a method present in X is overridden by both Y and Z but not by D then from which class D will inherit that method Y or Z. 113) Among LISTS,SETS,TUPLES which is faster? Sets 114) How Type casting is done in python? (Str -> int) s = “1234” # s is string i = int(s) # string converted to int 115) How python maintains conditional blocks? Python used indentation to differentiate and maintain blocks of code 116) Write a small code to explain repr() in python ? Repr gives the format that can be read by the compiler. Eg: y=2333.3 x=str(y) z=repr(y) print ” y :”,y print “str(y) :”,x print “repr(y):”,z ————- output y : 2333.3 str(y) : 2333.3 repr(y) : 2333.3000000000002 117) How to encrypt a string? str_enc = str.encode(‘base64’, ‘strict’) 118) Functions are objects -> Explain ? # can be treated as objects def print_new(val): return val.upper() print ( print_new(‘Hello’)) yell = print_new print yell(‘different string’) 119) Explain the synbtax to split a string in python? Str.split(separator,max_split) 120) How can you identify the data type of any variable in python? Use type(var) 121) What does MAP function in python do? map() returns a list of the results after it applys the function to each item in a iterable data type (list, tuple etc.) 122) What does the enum function in python do? When we need to print the vars index along when you iterate, we use the enum function to serve this purpose. 123) Explain assert in action? assert “py” == “PY”, “Strings are not eual” 124) How does pop function works in set data types? Pop deletes a random element from the set 125) Is Python open source? If so, why it is called so? Python is an open source programming language. Because Python’s source code (the code in which Python software is written) is open for all and anyone can have a look at the source code and edit. 126). Why Python is called portable? Because we can run Python in wide range of hardware platforms and has similar interfaces across all the platforms 127) How to give comments in Python? Using Hashes (#) at the starting of a line 128) How to create prompt in the console window? Using input function 129) How to write multiple statements in a single line in Python? Using semicolon between the statements 130) List out standard datatypes in Python Numbers, string, list, tuple, dictionary 131) Which standard datatype in Python is immutable? tuple 132) What is indexing? Explain with an example Indexing is the numbering of characters in string or items in list, tuple to give reference for them. It starts from 0. Str = “Python”. The index for P is 0, y is 1, t is 2 and goes on. 133).Which statement is used to take a decision based on the comparison? IF statement 134) List out atleast two loop control statements break, continue, pass 135) What is the result of pow(x,y) X raised to the power Y 136) What is the difference between while and for loop? While loops till the condition fails, for loops for all the values in the list of items provided. 137) Which method removes leading and trailing blanks in a string? strip – leading and trialing blanks, lstrip – leading blanks, rstrip – trailing blanks 138) Which method removes and returns last object of a list? list.pop(obj=lst) 139) What is argument in a function? Argument is the variable which is used inside the function. While calling the function we need to provide values to those arguments. 140) What is variable length argument in function? Function having undefined no. of arguments are called variable length argument function. While calling this function, we can provide any no. of arguments 141) What is namespace? Namespace is the dictionary of key-value pairs while key is the variable name and value is the value assigned to that variable. 142) What is module? Module is a file containing python code which can be re-used in a different program if it is a function. 143) Which is the default function in a class? Explain about it – _init_. It is called class contructor or initialization method. Python calls _init_ whenever you create a instance for the class 144) What is docstring? How to define it? docstring is nothing but a comment inside the block of codes. It should be enclosed inside “”” mark. ex: “”” This is a docstring ””” 145) What is the default argument in all the functions inside a class? Self 146) How to send a object and its value to the garbage collection? del objname 147) How to install a package and import? In DOS prompt, run pip install package_name and run import package_name in editor window in Python’s IDE. 148) Name the function which helps to change the files permission os.chmod 149) Which is the most commonly used package for data importing and manipulation? Pandas 150) Will python support object oriented? Yes, it will support by wrapping the code with objects. 151) IS python can be compatible with command prompt? Yes, it can be accessed through command prompt. 152) How Lists is differentiated from Tuples? List are slow, can be edited but Tuples are fast and cannot be edited. 153). Use of NUMPY package? It is fastest, and the package take care of the number calculations. 154). Uses of python? Pie charts, web application, data modeling, automation and Cluster data. 155) Does python interact with Database? Yes, it interfaces to most of the Databases. 156) Is python is intended oriented? Yes, it will throw error if it is not in seuence. 157) How is Garbage handled in python? It will be automatically handle the garbage after the variable is used. 158) How will you check python version? Using python –version. 159) How will you uit the python? Using exit() 160) Does Python has any command to create variable? No, just (x =244) 161) What is complex type in python? It is mixture of variable and number. 162) Casting in python? To make String use command str(2) = ‘2’ 163) What is strip in python? Used to remove white spaces in String 164) Other String literals? Lower, upper, len, split, replace. 165) Python operators? Arithmetic, Assignment, Comparison, Logical, Identity, Membership and Bitwise. 166) Membership operator in python? In and not in. 167) Lambda in python? Can take only one expression but any number of Argument. 168) Dict in python? It is something like key and value pair as Map in java. 169) Does python has classes? In python all are denoted as some classes. 170) Multi threading on python? It is a package in python and it use GIL to run the thread one after the other. But isn’t it being not good to use here. 171) What is python private heap space? It is a inbuild garbage collection like java and this space can be used by the developer. 172) Does python support inheritance? Yes, it supports all forms of inheritance single, multiple, hierarchical and multi-level 173) Benefits of Flask? It is light weight and independent package. Mainly a web micro framework. 174) How dir() function is used in python? The defined symbols are defined here. 175) Will exit method in python de allocate the global namespace? No, it has a specific mechanism which it follows as an individual portion. 176) Has python has monkey patching concept within? Yes of course, it does dynamic transactions during the run time of the program. 177) args vs kwargs? Args – don’t know how many arguments are used. Kwargs- don’t know how many keywords are used. 178) use of isupper keyword in python? This will prompt the upper keyword of any character in a string literal. 179) pickling vs unpickling? If the objects translated from string then it seems to be pickling If the String is dumped to objects then it seems to un picking 180) What is py checker in python? It is tool to uantitatively detects the bugs in source code. 181) What are the packages? NUMPY, SCIPY, MATLAB, etc 182) Pass in Python? IT is a namespace with no character and it can be moved to next object. 183) How is unit test done in python? It is done in form of Unittest. This does major of testing activity. 184) Python documentation is called? DoctString such as AI, Python jobs ,Machine learning and Charts. 185) Convert Sting to number and viceversa in python? Str() for String to number and oct() for number to string. 186) Local vs Global in python? Anything inside the function body is local and outside is global as simple as that. 187) How to run script in python? Use py command or python command to run the specific file in Unix. 188) What is unlink in python? This is used to remove the file from the specified path. 189) Program structure in python? Always import the package and write the code without indention 190) Pyramid vs Django? Both used for larger application and Django comes with a ORM framework. 191) Cookies in python? Sessions are known as cookies here it is used to reuest from one object to other. 192) Different types of reuest in python? Before reuest – it is used to passes without the arguments. After reuest – it is used to pass the reuest and response will be generated. Tear down reuest – it is used as same as past but it does not provide response always and the reuest cant be changed. 193) How is fail over mechanism works in python? Once the server shoots the fail over term then it automatically tends to remove the packet each on the solid base and then re shoot again on its own. Socket wont get removed or revoked from the orgin. 194) Dogpile mechanism explain? Whenever the server host the service and when it gets multiple hits from the various clients then the piles get generated enormously. This effect will be seems as Dogpile effect. This can be captured by processing the one hit per time and not allowed to capture multiple times. 195) What is CHMOD 755 in python? This will enhance the file to get all the privileges to read write and edit. 196) CGI in Python? This server mode will enable the Content-type – text/html\r\n\r\n This has an extension of .cgi files. This can be run through the cgi command from the cmd prompt. 197) Sockets explain? These are the terminals from the one end to the other using the TCP, UDP protocols this reuires domain, type, protocol and host address. Server sockets such as bind, listen and accept Client socket such as connect. 198) Assertions in python? This is stated as the expression is hits when we get the statement is contradict with the existing flow. These will throw the error based on the scenario. 199) Exceptions in python? This is as same as JAVA exceptions and it is denoted as the try, catch and finally this also provides the user defined expression. 200) What made you to choose python as a programming language? The python programming language is easy to learn and easy to implement. The huge 3rd party library support will make python powerful and we can easily adopt the python 201) what are the features of python? The dynamic typing Large third party library support Platform independent OOPs support Can use python in many areas like machine learning,AI,Data science etc.. 202) How the memory is managed in python? The private heap space is going to take care about python memory. whenever the object is created or destroyed the heap space will take care. As a programmer we don’t need to involve in memory operations of python 203) What is the process of pickling and unpicling? In python we can convert any object to a string object and we can dump using inbuilt dump().this is called pickling. The reverse process is called unpicling 204). What is list in python? A list is a mutable seuential data items enclosed with in and elements are separated by comma. Ex: my_list=] In a list we can store any kind of data and we can access them by using index 205) What is tuple in python? A tuple is immutable seuential data element enclosed with in () and are separated by comma. Ex: my_tuple=(1,4,5,’mouli’,’python’) We use tuple to provide some security to the data like employee salaries, some confidential information 206) Which data type you prefer to implement when deal with seuential data? I prefer tuple over list. Because the tuple accessing is faster than a list because its immutability 207) What are advantages of a tuple over a list? We can use tuple as a dictionary key because it is hash able and tuple accessing very fast compare to a list. 208) What is list comprehension and dictionary comprehension and why we use it? A list comprehension is a simple and elegant way to create a list from another list. we can pass any number of expressions in a list comprehension and it will return one value, we can also do the same process for dictionary data types Data= Ex: new_list = 209) What is the type of the given datatype a=1? a)int b)Tuple c)Invalid datatype d)String Ans:b 210) Which is the invalid variable assignment from the below? a)a=1,2,3 b)The variable=10 c)the_variable=11 d)none of the above Ans:b 211) Why do we use sets in python? Generally we use sets in python to eliminate the redundant data from any data. And sets didn’t accept any mutable data types as a element of a set Ex: my_set={123,456,’computer’,(67,’mo’)} 212) What are the nameless functions in python? The anonymous functions are called nameless functions in python. We can also call it as lambda function. The lambda functions can be called as a one liner and can be created instantly Syntax: lambda arguments: expression Ex: hello=lambda d:d-(d+1) To call the lambda function Hello(5) 213) What is map and filter in python? Map and filter are called higher order functions which will take another functions as an argument. 214) What is the necessity to use pass statement in python program? Pass is no operation python statement. we can use it while we are implementing the classes or functions or any logic. If class is going be define later in the development phase we can use pass statement for the class to make it syntactically make it valid. Ex: def library(): Pass 215) What is *kwargs and **kwargs? Both are used in functions. both are allowed to pass variable number of arguments to a function only difference is *kwargs is used for non-key word arguments and **kwargs is used for key word arguments Ex: def kwargs(formal_arg, *kwargv): print(“first normal arg:”, formal_arg) for arg in kwargv: print(“another arg through *argv:”, arg) kwargs(‘mouli’, ‘ramesh’, ‘rajesh’, ‘kanna’) 216) Explain about negative indexing? Negative indexing is used in python seuential datatypes like list,string,tuple etc We can fetch the element from the back with out counting the list index Ex: list1 217) What is file context manager? To open a file in safe mode we use WITH context manager. This will ensure the file crashing from some exceptions. we don’t need to close the file explicitly Ex: with open(‘sample.txt’,’w’) as f: Pass 218) Explain between deep and shallow copy? The deep copy , copy the object with reference so that if we made any changes on the original copy the reference copy will be effected, shallow copy ,copy the object in a separate memory so that if we do any changes on original it won’t effect the shallow copy one 219) How can you make modules in python? First we need to save the file with somename.py Second import the somename.py in the newfile.py, so that we can access the somename.py functions in the newfile.py. so that somename.py acts as a module. Even we can share our module to the rest of the world by registering to PYPY community 220) Explain about default database with python? SLite3 comes with python3. It is light weight database for small scale of application 221) What are different modes in file operations? There are 3 modes in python file operations read, write and append sometimes we can do both at a time. read(),readline(),readlines() are the inbuilt functions for reading the file write() is inbuilt function for writing to the file 222) What is enumerate() explain its uses? Enumerate is a built in function to generate the index as we desired in the seuential datatypes Ex: for c ,i in enumerate(data,p): Print(c,i) Here p is optional if we don’t want it we can eliminate it 223) Can we use else with for loop in python? Yes we can use. once all the for loop is successfully executed the else part is going to execute, If there are any error occurs or any break happened in the loop then the else is not going to execute Ex: for I in list1: print(i) Else: print(execution done) even we can use else with while also 224) What is type() and id() will do? The type() will give you the information about datatype and id() will provide you the memory location of the object 225) What is decorators? The decorators are special functions which will very useful when tweaking the function or class.it will modify the functionality of another function. 226) Explain about different blocks in exception handling? There are three main blocks in python exception handling Try Except Finally In the try block we will write all the code which can be prone to error, if any error occurred in this block it will go to the except block. If we put finally block also the execution will hit the finally block. 227) Explain inheritance in python? Inheritance will allow the access to the child call meaning it can access the attributes and methods of the base. There are many types in the inheritance Single inheritance: in this one, have only one base class and one derived class Multilevel inheritance: there can be one or more base classes and one more derived classes to inherit Hierarchical: can derive any number of child classes from single base class Multiple: a single derived can be inherited from any number of base classes 29.write sorting algorithm in python for given dataset= using list comprehension x= print(x.sort()) 228) Explain about multi-threading concept in python? Multi-threading process can be achieved through the multiprocess inbuilt module. GIL(global interpreter lock ) will take care about the multiprocessing in python. simultaneously there are several threads can be run at same time. The resource management can be handled by GIL. 229) Can we do pattern matching using python? Yes, we can do it by using re module. like other programming languages python has comes with powerful pattern matching techniue. 230) What is pandas? Pandas is data science library which deal with large set of data. pandas define data as data frame and processes it. Pandas is a third party library which we need to install. 231) What is pip? Pip is a python package installer. Whenever we need third party library like paramiko,pandas etc We have to use pip command to install the packages Ex: pip install paramiko 232) What is the incorrect declaration of a set? a)myset={} b)myset=set() c)myset=set((1,2,3)) d)myset={1,2,3} Ans:a 233) What is OS module will do in python? OS module is giving access to python program to perform operating system operations like changedirectory, delete or create. Ex: import os os.cwd() 234) What is scheduling in threading? Using scheduling we can decide which thread has to execute first and what is the time to execute the thread. And it is highly dynamic process 235) What is the difference between module and package? A package is folder which can have multiple modules in it. We can import module by its package name.module name 236) How we can send email from python? We can use smtplib inbuilt module to define smtp client, that can be used to send email 237) What is TKIner? TKIner is a python inbuilt library for developing the GUI 238) How can you prevent abnormal termination of a python program We can prevent the abnormal termination by using the exception handling mechanism in python. Try , except and finally are the key words for handling the exception. we can raise our own exceptions in the python. They are called user exceptions 239) what module is used to execute linux commands through the python script and give us with one example We can use OS module to execute any operation system commands. We have to import the OS module first and then give the commands Ex: import os Print(os.system(‘nslookup’+’127.10.45.00’)) 240) what is the process to set up database in Django First we need to edit the settings.py module to set up the database. Django comes with SLite database by default, if we want to continue with default database we can leave settings.py as it is. If we decide to work with oracle or other kind of databases like oracle your database engine should be ‘django.db.backends.oracle’. if it is postgresl then the engine should ‘django.db.backends.postgresl_psycopg2’. We can add settings like password, name host etc. 241) what is Django template A django template is a simple text file which is used to create HTML,CSV or XML. A template contains variables that is replaced with values when we evaluates it 242) what is the uses of middleware in Django? Middleware is responsible for user authentication, session management . 243) what is Django architecture Django architecture contains models ,views, templates and controller The model describes the database schema and data structure. the views retrieves data from model and pass it to the template. Templates are described how the user see it. controller is the logic part and heart of the Django 244) List some of the data science libraries in python NumPy Pandas SciPy Matplotlib 245) How do substitute a pattern in a string using re module Import re >>> re.sub(‘’, ‘o’, ‘Space’) ‘Spooe’ >>> re.sub(‘’, ‘n’, re.sub(‘’, ‘o’, ‘Space’)) ‘Spoon’ 246) What is random module will do in python and what are the functions we can apply on random module Random module will gives the random number from the specific range. Every time we execute we will get the random number Randrange() Randint() Choice() Shuffle() Uniform() Are some of the useful functions in random module 247) What are the noted modules of python in terms of networking Paramiko, netmiko, pexpect etc These module will create a ssh connection between server and the program 248) What is beautifulSoup module will do in python? We are using the module for pulling the data from HTML and XML files 249) What is reuests module will do? It is a python http library. The aim of the reuests module is to make http reuests simpler and more human friendly Ex: Import reuests r = reuests.get(‘https://api.github.com/user’, auth=(‘user’, ‘pass’)) r.status_code 200 >>> r.headers ‘application/json; charset=utf8’ >>> r.encoding ‘utf-8′ >>> r.text # doctest: +ELLIPSIS u'{“type”:”User”…’ >>> r.json() # doctest: +ELLIPSIS {u’private_gists’: 419, u’total_private_repos’: 77, …} 250) What are the basic datatypes in python? Python datatypes include int, float, strings, lists, tuples, sets, dictionaries. 251) How Manages to Python Handle Memory Management? Python is a separate on heaps to keep its memory. So the heap contains all the Python information and these data structures. And it’s the Python created handler that manages the Individual heap. Python employs a built-in garbage receiver, which salvages all the available memory including offloads it to some heap space. 252) What is means by string Python? A string in Python is a mixture of the alpha-numeric volume of characters. They are clear of objects Volume. It suggests that both don’t help move once all get assigned a value. Python provides to programs of join(), replace(), or split() to alter strings variable. 253) What does the meaning of Slicing in python? Python Slicing is defined as Lists of Tuples and Arrays Volume function. The Lists element function has a default bit fo the functionality while slicing. If there is a no conseuence of before that first colon, it expects to begin at the start index of the list. 254) Definition of %S In Python? Python it has to been guide for formatting of any value into a string volume function. It may include uite complex characters. It’s One of the popular usages of the start contents into a string including the %s form specifier. The %S formatting helps Python in a similar variable volume syntax as the C function printf(). 255) what does a function of python programming? A function is an object which describes a block of the system and is a reusable object. It takes modularity to a performance code program and a higher level of code reusability. Python has to give us several built-in functions Volume such as print() function volume and it gives the ability to perform a user-defined function. 256) How to write a functioning volume for python? Step-1: To begin the function Volume of start writing the function with the keyword and then specify the Volume function name. Step-2: We can immediately give the reasons and enclose them doing the parentheses. Step-3: After pushing an enter, we can do it determine the coveted Python records for execution. 257) What is means by Call function in Python? A python function value gets treated because of a callable object. It can provide any thoughts value and also pass a value or increased values into the model of a tuple. Apart from this function, Python should additional constructs, such as being groups or the class instances fit in the related category. 258) How to use of return keywords in python? The purpose of a value function get the inputs and return value of some output. The return value of is a Python statement if it’s we can relate to using for sending content following to its caller. 259) What is meant by“Call By Value” In Python? In call-by-value, that argument to be valued expression or value becomes connected to the particular variable in this function. Python command treats that variable being confined within the function-level field. Any changes done to this variable will continue local and order reflect outside the function. 260) What does means by “Call By Reference” In Python? The Call-by-reference we pass as an argument by reference volume, then it is possible because of an absolute source on the use, first then some simple copy. In such any case, any change to the discussion instructions further is obvious to the caller. 261) Difference between Pass and Continue In Python? The continue report executes the loop value to return from the following emphasis. On the opposite, that passing record instructs to make nothing, including the remainder from the code effects as usual. 262) What is meant by R strip() In Python? Python gives the r-strip() system to increases this string value function but allows avoid this whitespace symbols of that end. This r-strip() transmits that numbers value function of right end based upon particular argument value a string specifying the group of numbers to get excluded. 263) What does defined by whitespace in python? Whitespace is representing the characters string value function that we practice for spacing moreover separation. They maintain the“empty” value function symbol. In Python, it could move some tab or space. 264) What is defined Isalpha() In Python? Python has been provided that built-in isalpha() value function for each string manipulating purpose. It reflects the True value function if all types in this string value function are of alphabet type number, else value function it returns False. 265) What does making the CPython Different From Python? Jython means an implementation from some Python programming language that can operate code using on this Java platform. Jython is uiet as compared to CPython and reuires agreement with CPython libraries. A Python implementation is written in C# getting a Microsoft’s .NET framework. 266) Which is the package Fastest Form Of Python? PyPy gives maximum agreement while utilizing CPython implementation as increasing its performance. The tests verified that PyPy is almost five times faster than uniue CPython. 267) What does the meaning of GIL In Python Language? Python is helped to GI(thats means by the global interpreter) which operates some mutex done to ensure introduction into Python objects, synchronizing multiple threads of running these Python bytecodes at the same time. 268) How do Python Thread Safe? Python ensures the reliable path of the threads. It does this GIL mutex to secure synchronization. If a thread fails the GIL lock through any time, when you must to get this system thread-safe. 269) How Does determine the Python Manage The Memory? Python performs a property manager within which operates any of its articles also data structures. This heap manager makes that allocation/de-allocation from heap space to objects. 270) What is a means by “Tuple In Python”? A tuple is a group of specific data structure under Python is immutable. They mean similar to progressions, really prefer the lists. Also, that tuples follow parentheses as including, but these programs have suare sections in their syntax. 271) What does means by split do in Python? This is the opposite of order which mixes or combines strings within one. To do this, you practice this split function value. What it takes is divided or develop up a string and attach that data into each order collection using a specified separator. If none separator is specified while you charge against specific function, whitespace order signify done by default. 272) How do you convert a string to in python? Use the “int” String function value to convert the number to an integer value. Add five value to the integer. Then, the “str” function value it’s to converts the integer function value to a string value function that Python concatenates and print the output value of the answer. 273) How do you reverse any string in Python? This is continued the reverse value function part syntax. It goes outcomes too by doing – by leaving start value and end off value and defining a step of -1, it reverses value function a string function. 274) What does by Python a scripting language? Python is identified as a scripting language because it is an interpreted language also because that is simple to record scripts in it. A defined python communication programming is a language whose programs have to be obtained before they can be run. 275) What language is Python based on? Since largest recent OS continue written in C, compilers/editors before improved high-level languages exist also written in C. Python continues an exception – its various popular/”traditional” implementation means described CPython more is written in C. 276) What is the best free website to learn Python? Python.org. is one the best Python Software Foundation’s official website is further one of the valuable free source locations.SoloLearn- If it refers to a modular, crash-course-like information environment, SoloLearn gives an excellent, step-by-step knowledge program for beginners, TechBeamers , Hackr.io, Real Python. 277) Difference between Python and Java? The Two biggest difference languages signify that the Java is one the statically typed program coding language and Python is one of the dynamical typed. Python is very heavily code programming language but dynamically typed. In certain means types in one code remain confined to strongly Copied something at runtime. 278) How Can you declare the variables function in Python? In Java or C, every variable must be certified before it can be used. Declaring the variable means connecting it to a data type value function. Declaration of variables is expected in Python. You can specify an integer value function to a variable, use it is an integer value function for a while and when specifying a string to the variable function. 279) How to declare the variables function in Python? Python is defined as a dynamically typed variable, which indicates that you have to declare what type each function variable is. In Python, variables do a storage placeholder during texts and numbers variable. It needs to convert one name so that you remain ualified to get this again. The variable does forever assign with an eual sign, replaced by the value of the variable function. 280) How do you reverse the string in python? There is no such inbuilt function for this. The Easiest way for reversing the string in python is using slice which steps backwards, -1. For example: txt = “Hello World” print(txt). 281) WAP to find the given string in the line? This is the WAP for finding the given string in line. Str = ‘Hello world’ If ‘hello’ in str: Print ‘string found’. 282) What is class variable in python? The Class variable are also known as static variables. These variables are shared by all objects. In Python the variables that are assigned the value in class declaration are known as class variables. 283) What is class in Python? The python is “object oriented language”. Almost all the codes of this language are implemented using a special construct called Class. In simple words, “Class” is an object constructer in Python. 284) How can you handle multiple exception in python? To handle multiple exception in python you can use try statement. You can also use these blocks: The try/except blocks The finally blocks The raise keywords Assertions Defining your own exception 285) Can we write else statement try block in python? Yes, it is possible to write else statement try block. try: operation_that_can_throw_ioerror() except IOError: handle_the_exception_somehow() else: # we don’t want to catch the IOError if it’s raised another_operation_that_can_throw_ioerror() finally: something_we_always_need_to_do(). 286) Does Python have do-while loop statements? No, Python doesn’t have any do-while loop statements. 287) What is the difference between range and xrange in Python? In python the range and xrange are two functions that are used repeat number of time in for loops. The major difference between rang and xrange is that the xrange returns the xrange object while the range returns a python list objects. The xrange is not capable for generating the static list at run-time. On the other hand range can do that. 288) Is it possible to inherit one class from another class? Yes, we can inherit one class from another class in python. 289) Name different types of inheritance in python? The inheritance refers to the capability of on class to derive the properties from other class. In python, there are two major types of inheritance. Multiple Inheritance Multilevel Inheritance 290) What is polymorphism? The polymorphism in python refers to various types of respond to the same function. In Greek language the word poly means “many” and morphism means “forms”. This means that the same function name is being used on objects of different types. 291) How do you convert string as a variable name in python? The simplest way to convert string as a variable name is by using vars(). 292) Why do we want to use break statement in while-loop? While-loop can convert into the infinite loop if you don’t use break statement. 293) Why we are using Def keyword for method? The Def keyword in python is used to form a new user-defined function. The def keywords mark the beginning of function header. The functions are the objects through which one can easily organize the code. 294) Why are we using self as first argument? The first argument represents the current instance of the class. The first argument is always called self. With the use of “self” keyword one can easily access the characteristics and methods of the class in python. 295) Why we are using a Python Dictionary? There is huge collection of data values in the python dictionary. These dictionaries are accessed to retrieve the value of the keys that unknown to the users. There is a key: value pair provided in the dictionary which makes it more optimized. 296) What are the use of tuples in Python? A tuple in python is a series of immutable Python objects. These tuples are similar to the list that are used for organizing data to make it easier to understand. If Python has created a tuple in memory, it difficult to change them. 297) What are the use of sets in Python? The Python Set is the collection objects similar to lists and dictionaries. All the elements should be original and uniue and must be immutable. The python sets in comparison with list provides highly optimized method for ensuring whether a specific element is contained in the set. 298) Does Python supports hybrid inheritance? No, python doesn’t support hybrid inheritance. But we can use straight method and round diamond method we can achieve it. 299) What is the uses of middleware in Django? Middleware is responsible for user authentication, session management . 300) Explain Deep Copy in Python There are some values copied already. To store those copied values, Deep copy is used. Unlike Shallow copy, Deep copy will not copy the reference pointers. 301) Define the usage of split If you want to separate a provided string in Python, use split() function. 302) What is the keyword to import a module in Python? Use the keyword ‘import’ to import the modules in Python. 303) List out the different types of inheritance available in Python Hierarchical inheritance, Multi-level inheritance, Multiple inheritance, and Single Inheritance are the four types inheritance available in Python. 304) Define monkey patching You can make dynamic modifications to a module or class during the run-time. This process is called monkey patching in Python. 305) Explain encapsulation Binding the data and code together is known as encapsulation. Example of encapsulation is a Python class. 306) Define Flask in Python Flask, a microframework principally constructed for a minor application with easier reuirements. External libraries must be used in Flask and flask is always ready to use state. 307) Define Pyramid in Python For larger application, you can make use of Pyramid and this is hefty configurable concept. Pyramid affords suppleness and permits the developer to employ the appropriate tools for their assignment. 308) Define Django in Python Similar to Pyramid, Django is built for larger applications and ORM is included. 309) Provide the Django MVT Pattern Django Pattern 310) Why to use Python numpy instead o f lists? Python numpy is convenient, less memory and rapid when compared to lists. Hence, it is better to use python numpy. 311) Mention the floor division available in Python Double-slash (//) is the floor division in Python. 312) Is there any maximum length expected for an identifier? No, there is no maximum length expected for an identifier as it can have any length. 313) Why do we say “a b c = 1000 2000 3000” is an invalid statement in Python? We cannot have spaces in variable names and hence a b c = 1000 2000 3000 becomes invalid statement. 314) Mention the concept used in Python for memory managing Python private heap space is the one used to manage memory. 315) What are the two (2) parameters available in Python map? Iterable and function are the two (2) parameters available in Python map 316) Explain “with” statement in Python As soon as there is a block of code, you can open and close a file using “with” statement in Python. 317) What are the modes to open a file in Python? read–write mode (rw), write-only mode (w), and read-only mode (r) is the three (3) modes to open a file in Python. 318) Try to provide the command to open a file c:\welcome.doc for writing Command to open a file for writing f= open(“welcome.doc”, “wt”) 319) Explain Tkinter in Python An inbuilt Python module helpful in creating GUI applications is known as Tkinter. 320) What does the keyword do in python? The yield keyword can turn ant function into a generator. It works like a standard return keyword. But it will always return a generator object. A function can have multiple calls the keyword. Example: def testgen(index): weekdays = yield weekdays yield weekdays day = testgen(0) print next(day), next(day) Output: Sun mon PYTHON Interview Questions with Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes